Sticking together: building a biofilm the Bacillus subtilis way
- PMID: 23353768
- PMCID: PMC3936787
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro2960
Sticking together: building a biofilm the Bacillus subtilis way
Abstract
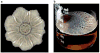
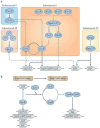
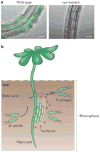
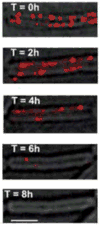
Biofilms are ubiquitous communities of tightly associated bacteria encased in an extracellular matrix. Bacillus subtilis has long served as a robust model organism to examine the molecular mechanisms of biofilm formation, and a number of studies have revealed that this process is regulated by several integrated pathways. In this Review, we focus on the molecular mechanisms that control B. subtilis biofilm assembly, and then briefly summarize the current state of knowledge regarding biofilm disassembly. We also discuss recent progress that has expanded our understanding of B. subtilis biofilm formation on plant roots, which are a natural habitat for this soil bacterium.
Figures

References
-
- Cohn F. Untersuchungen über bacterien. IV. Beiträge zur biologie der Bacillen. Beiträge zur biologie der Pflanzen. 1877;7:249–276.
-
- Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:95–108. - PubMed
-
- Stewart PS, Franklin MJ. Physiological heterogeneity in biofilms. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6:199–210. - PubMed
-
- Davies D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:114–122. - PubMed
-
- Mah TF, O’Toole GA. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9:34–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

