Epigenetic silencing of retinoblastoma gene regulates pathologic differentiation of myeloid cells in cancer
- PMID: 23354483
- PMCID: PMC3578019
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2526
Epigenetic silencing of retinoblastoma gene regulates pathologic differentiation of myeloid cells in cancer
Abstract
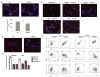
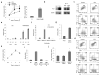
Two major populations of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), monocytic MDSCs (M-MDSCs) and polymorphonuclear MDSCs (PMN-MDSCs) regulate immune responses in cancer and other pathologic conditions. Under physiologic conditions, Ly6C(hi)Ly6G(-) inflammatory monocytes, which are the normal counterpart of M-MDSCs, differentiate into macrophages and dendritic cells. PMN-MDSCs are the predominant group of MDSCs that accumulates in cancer. Here we show that a large proportion of M-MDSCs in tumor-bearing mice acquired phenotypic, morphological and functional features of PMN-MDSCs. Acquisition of this phenotype, but not the functional attributes of PMN-MDSCs, was mediated by transcriptional silencing of the retinoblastoma gene through epigenetic modifications mediated by histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC-2). These data demonstrate a new regulatory mechanism of myeloid cells in cancer.
Figures


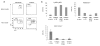



Comment in
-
Myeloid-cell differentiation redefined in cancer.Nat Immunol. 2013 Mar;14(3):197-9. doi: 10.1038/ni.2539. Nat Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23416669 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

