Recent evolutionary radiation and host plant specialization in the Xylella fastidiosa subspecies native to the United States
- PMID: 23354698
- PMCID: PMC3623259
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03208-12
Recent evolutionary radiation and host plant specialization in the Xylella fastidiosa subspecies native to the United States
Abstract
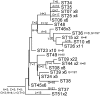
The bacterial pathogen, Xylella fastidiosa, infects many plant species in the Americas, making it a good model for investigating the genetics of host adaptation. We used multilocus sequence typing (MLST) to identify isolates of the native U.S. subsp. multiplex that were largely unaffected by intersubspecific homologous recombination (IHR) and to investigate how their evolutionary history influences plant host specialization. We identified 110 "non-IHR" isolates, 2 minimally recombinant "intermediate" ones (including the subspecific type), and 31 with extensive IHR. The non-IHR and intermediate isolates defined 23 sequence types (STs) which we used to identify 22 plant hosts (73% trees) characteristic of the subspecies. Except for almond, subsp. multiplex showed no host overlap with the introduced subspecies (subspecies fastidiosa and sandyi). MLST sequences revealed that subsp. multiplex underwent recent radiation (<25% of subspecies age) which included only limited intrasubspecific recombination (ρ/θ = 0.02); only one isolated lineage (ST50 from ash) was older. A total of 20 of the STs grouped into three loose phylogenetic clusters distinguished by nonoverlapping hosts (excepting purple leaf plum): "almond," "peach," and "oak" types. These host differences were not geographical, since all three types also occurred in California. ST designation was a good indicator of host specialization. ST09, widespread in the southeastern United States, only infected oak species, and all peach isolates were ST10 (from California, Florida, and Georgia). Only ST23 had a broad host range. Hosts of related genotypes were sometimes related, but often host groupings crossed plant family or even order, suggesting that phylogenetically plastic features of hosts affect bacterial pathogenicity.
Figures


References
-
- Maiden MCJ, Bygraves JA, Feil E, Morelli G, Russell JE, Urwin R, Zhang Q, Zhou JJ, Zurth K, Caugant DA, Feavers IM, Achtman M, Spratt BG. 1998. Multilocus sequence typing: a portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95: 3140–3145 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maiden MCJ. 2006. Multilocus sequence typing of bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 60: 561–588 - PubMed
-
- Nunney L, Elfekih S, Stouthamer R. 2012. The importance of multilocus sequence typing: cautionary tales from the bacterium Xylella fastidiosa. Phytopathology 102: 456–460 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

