Cloning and regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid biosynthesis
- PMID: 2335522
- PMCID: PMC4451855
Cloning and regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid biosynthesis
Abstract
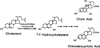
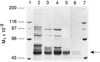
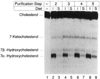
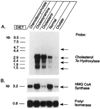
The rate-limiting step in bile acid biosynthesis is catalyzed by the microsomal cytochrome P-450 cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase (7 alpha-hydroxylase). The expression of this enzyme is subject to feedback regulation by sterols and is thought to be coordinately regulated with enzymes in the cholesterol supply pathways, including the low density lipoprotein receptor and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and synthase. Here we report the purification of rat 7 alpha-hydroxylase and the determination of a partial amino acid sequence. Oligonucleotides derived from peptide sequence were used to clone a full-length cDNA encoding 7 alpha-hydroxylase. DNA sequence analysis of the cDNA revealed a 7 alpha-hydroxylase protein of 503 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 56,890 which represents a novel family of cytochrome P-450 enzymes. Transfection of a 7 alpha-hydroxylase cDNA into simian COS cells resulted in the synthesis of a functional enzyme whose activity was stimulated in vitro by the addition of rat microsomal cytochrome P-450 reductase protein. RNA blot hybridization experiments indicated that the mRNA for 7 alpha-hydroxylase is found only in the liver. The levels of this mRNA increased when bile acids were depleted by dietary cholestyramine and decreased when bile acids were consumed. Dietary cholesterol led to an increase in 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA levels. The enzymatic activity of 7 alpha-hydroxylase paralleled the observed changes in mRNA levels. These results suggest that bile acids and sterols are able to alter the transcription of the 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene and that this control explains the previously observed feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis.
Figures



References
-
- Dietschy JM, Wilson JD. N. Engl. J. Med. 1970;282:1128–1138. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. Science. 1986;232:34–47. - PubMed
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. J. Lipid. Res. 1980;21:505–517. - PubMed
-
- Carey MC. In: The Liver: Biology and Pathobiology. Arias IM, Popper H, Schachter D, Shafritz DA, editors. New York: Raven Press; 1982. pp. 429–465.
-
- Südhof TC, Russell DW, Brown MS, Goldstein JL. Cell. 1987;48:1061–1069. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

