Muscle metaboreflex-induced coronary vasoconstriction limits ventricular contractility during dynamic exercise in heart failure
- PMID: 23355344
- PMCID: PMC3625893
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00879.2012
Muscle metaboreflex-induced coronary vasoconstriction limits ventricular contractility during dynamic exercise in heart failure
Abstract
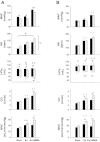
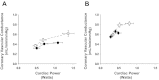
Muscle metaboreflex activation (MMA) during dynamic exercise increases cardiac work and myocardial O2 demand via increases in heart rate, ventricular contractility, and afterload. This increase in cardiac work should lead to metabolic coronary vasodilation; however, no change in coronary vascular conductance occurs. This indicates that the MMA-induced increase in sympathetic activity to the heart, which raises heart rate, ventricular contractility, and cardiac output, also elicits coronary vasoconstriction. In heart failure, cardiac output does not increase with MMA presumably due to impaired ability to improve left ventricular contractility. In this setting actual coronary vasoconstriction is observed. We tested whether this coronary vasoconstriction could explain, in part, the reduced ability to increase cardiac performance during MMA. In conscious, chronically instrumented dogs before and after pacing-induced heart failure, MMA responses during mild exercise were observed before and after α1-adrenergic blockade (prazosin 20-50 μg/kg). During MMA, the increases in coronary vascular conductance, coronary blood flow, maximal rate of left ventricular pressure change, and cardiac output were significantly greater after α1-adrenergic blockade. We conclude that in subjects with heart failure, coronary vasoconstriction during MMA limits the ability to increase left ventricular contractility.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Muscle metaboreflex-induced coronary vasoconstriction functionally limits increases in ventricular contractility.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010 Aug;109(2):271-8. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01243.2009. Epub 2010 Apr 22. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010. PMID: 20413426 Free PMC article.
-
Exaggerated coronary vasoconstriction limits muscle metaboreflex-induced increases in ventricular performance in hypertension.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;312(1):H68-H79. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00417.2016. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27769997 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle metaboreflex-induced increases in cardiac sympathetic activity vasoconstrict the coronary vasculature.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007 Jul;103(1):190-4. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00139.2007. Epub 2007 May 3. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007. PMID: 17478607
-
Altered reflex cardiovascular control during exercise in heart failure: animal studies.Exp Physiol. 2006 Jan;91(1):73-7. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2005.031179. Epub 2005 Sep 22. Exp Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16179406 Review.
-
Cardiocirculatory dynamics in the normal and failing heart.Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:455-76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.002323. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981. PMID: 6452090 Review.
Cited by
-
Muscle metaboreflex-induced vasoconstriction in the ischemic active muscle is exaggerated in heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Jan 1;314(1):H11-H18. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00375.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28939649 Free PMC article.
-
Blood flow restriction training and the exercise pressor reflex: a call for concern.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Nov;309(9):H1440-52. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00208.2015. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26342064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attenuated muscle metaboreflex-induced pressor response during postexercise muscle ischemia in renovascular hypertension.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015 Apr 1;308(7):R650-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00464.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25632024 Free PMC article.
-
Neural control of circulation and exercise: a translational approach disclosing interactions between central command, arterial baroreflex, and muscle metaboreflex.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Aug 1;309(3):H381-92. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00077.2015. Epub 2015 May 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26024683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sympathetic Overactivity in Chronic Kidney Disease: Consequences and Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Aug 2;18(8):1682. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081682. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28767097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adreani CM, Kaufman MP. Effect of arterial occlusion on responses of group III and IV afferents to dynamic exercise. J Appl Physiol 84: 1827–1833, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Ansorge EJ, Augustyniak RA, Perinot RL, Hammond RL, Kim JK, Sala-Mercado JA, Rodriguez J, Rossi NF, O'Leary DS. Altered muscle metaboreflex control of coronary blood flow and ventricular function in heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288: H1381–H1388, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Ansorge EJ, Shah SH, Augustyniak R, Rossi NF, Collins HL, O'Leary DS. Muscle metaboreflex control of coronary blood flow. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283: H526–H532, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Aronow WS, Lurie M, Turbow M, Whittaker K, Van CS, Hughes D. Effect of prazosin vs placebo on chronic left ventricular heart failure. Circulation 59: 344–350, 1979 - PubMed
-
- Augustyniak RA, Collins HL, Ansorge EJ, Rossi NF, O'Leary DS. Severe exercise alters the strength and mechanisms of the muscle metaboreflex. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280: H1645–H1652, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

