Compromised respiratory function in lethal influenza infection is characterized by the depletion of type I alveolar epithelial cells beyond threshold levels
- PMID: 23355384
- PMCID: PMC3627938
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00343.2012
Compromised respiratory function in lethal influenza infection is characterized by the depletion of type I alveolar epithelial cells beyond threshold levels
Abstract
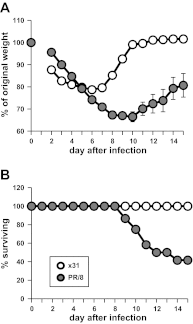
During influenza virus infection, it is unclear how much alveolar cell loss can be tolerated before the host succumbs to the disease. We sought to define relevant correlates of disease severity in the mouse influenza model, hypothesizing that a susceptibility threshold exists for alveolar epithelial cell loss. We compared lung pathology, virus spread, alveolar epithelial cell depletion, arterial blood oxygenation, physiological responses measured by unrestrained plethysmography, and oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production by gas analysis in mice at intervals after infection with virus strains and doses that cause mild (x31) or severe (PR/8) influenza. Both mild and severe infections showed similar degrees of lung damage and virus dissemination until day 6 after inoculation but diverged in survival outcomes from day 9. Day 6 PR/8-infected mice had normal respiratory and gas exchange functions with 10% type I cell loss. However, day 10 PR/8-infected mice had 40% type I cell loss with a concomitant drastic decreases in tidal and minute volumes, Vo(2), Vco(2), and arterial blood oxygenation, compared with a maximum 3% type I cell loss for x31 on day 10 when they recovered body weight and respiratory functions. Alterations in breaths per minute, expiratory time, and metabolic rate were observed in both infections. A threshold for maintenance of proper respiratory function appears to be crossed once 10% of alveolar type I cells are lost. These data indicate that lethality in influenza virus infection is a matter of degree rather than quality.
Figures




References
-
- Abdul-Careem MF, Mian MF, Yue G, Gillgrass A, Chenoweth MJ, Barra NG, Chew MV, Chan T, Al-Garawi AA, Jordana M, Ashkar AA. Critical role of natural killer cells in lung immunopathology during influenza infection in mice. J Infect Dis 206: 167–177, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Bates J, Irvin C, Brusasco V, Drazen J, Fredberg J, Loring S, Eidelman D, Ludwig M, Macklem P, Martin J, Milic-Emili J, Hantos Z, Hyatt R, Lai-Fook S, Leff A, Solway J, Lutchen K, Suki B, Mitzner W, Pare P, Pride N, Sly P. The use and misuse of Penh in animal models of lung disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 31: 373–374, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Bruder D, Srikiatkhachorn A, Enelow RI. Cellular immunity and lung injury in respiratory virus infection. Viral Immunol 19: 147–155, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

