The effect of including the C2 insert of nonmuscle myosin II-C on neuritogenesis
- PMID: 23355468
- PMCID: PMC3597820
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.417196
The effect of including the C2 insert of nonmuscle myosin II-C on neuritogenesis
Abstract
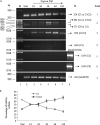
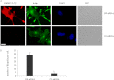
The functional role of the C2 insert of nonmuscle myosin II-C (NM II-C) is poorly understood. Here, we report for the first time that the expression of the C2 insert-containing isoform, NM II-C1C2, is inducible in Neuro-2a cells during differentiation both at mRNA and protein levels. Immunoblot and RT-PCR analysis reveal that expression of NM II-C1C2 peaks between days 3 and 6 of differentiation. Localization of NM II-C1C2 in Neuro-2a cells suggests that the C2 insert-containing isoform is localized in the cytosol and along the neurites, specifically at the adherence point to substratum. Inhibition of endogenous NM II-C1C2 using siRNA decreases the neurite length by 43% compared with control cells treated with nonspecific siRNA. Time lapse image analysis reveals that neurites of C2-siRNA-treated cells have a net negative change in neurite length per minute, leading to a reduction of overall neurite length. During neuritogenesis, NM II-C1C2 can interact and colocalize with β1-integrin in neurites. Altogether, these studies indicate that NM II-C1C2 may be involved in stabilizing neurites by maintaining their structure at adhesion sites.
Figures






References
-
- da Silva J. S., Dotti C. G. (2002) Breaking the neuronal sphere. Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in neuritogenesis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 694–704 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad F. J., Hughey J., Wittmann T., Hyman A., Greaser M., Baas P. W. (2000) Motor proteins regulate force interactions between microtubules and microfilaments in the axon. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 276–280 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

