Acute stroke in a patient with advanced uraemia: should thrombolysis be given?
- PMID: 23355564
- PMCID: PMC3604296
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-007307
Acute stroke in a patient with advanced uraemia: should thrombolysis be given?
Abstract
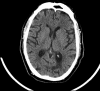
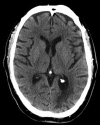
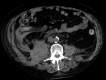
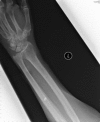
A 65-year-old gentleman with stage 5 chronic kidney disease developed an acute posterior circulation stroke, which was treated with intravenous thrombolytic therapy. This was complicated by a retroperitoneal haemorrhage. The patient made an excellent neurological recovery and was discharged to home, independently mobile, having been established on haemodialysis. This case highlights the challenges of managing acute ischaemic stroke in patients with advanced uraemia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Posterior vs. anterior circulation infarction: demography, outcomes, and frequency of hemorrhage after thrombolysis.Int J Stroke. 2015 Dec;10(8):1224-8. doi: 10.1111/ijs.12626. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Int J Stroke. 2015. PMID: 26310390
-
Safety and efficacy of rt-PA treatment for acute stroke in pseudoxanthoma elasticum: the first report.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021 Jan;51(1):176-179. doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02150-3. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021. PMID: 32458317
-
[Thrombolytic therapy in patients with acute brain infarction: favorable preliminary results in Maastricht].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2000 May 27;144(22):1062-9. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2000. PMID: 10850109 Dutch.
-
Intravenous thrombolytic therapy for acute ischemic stroke.N Engl J Med. 2011 Jun 2;364(22):2138-46. doi: 10.1056/NEJMct1007370. N Engl J Med. 2011. PMID: 21631326 Review. No abstract available.
-
Acute ischaemic stroke in patients aged 80 years and older: focus on the tolerability of thrombolytic agents.Drugs Aging. 2008;25(2):95-103. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200825020-00002. Drugs Aging. 2008. PMID: 18257597 Review.
References
-
- Khella S, Bleicher MB. Stroke and its prevention in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2007;2:1343–51 - PubMed
-
- Seliger SL, Gillen DL, Tirschwell D, et al. Risk factors for incident stroke among patients with end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2003;14:2623–31 - PubMed
-
- Seliger SL, Gillen DL, Longstreth WT, Jr, et al. Elevated risk of stroke among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int 2003;64:603–9 - PubMed
-
- Hedges SJ, Dehoney SB, Hooper JS, et al. Evidence-based treatment recommendations for uraemic bleeding. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2007;3:138–53 - PubMed
-
- De Keyser J, Gdovinova Z, Uyttenboogaart M, et al. Intravenous alteplase for stroke: beyond the guidelines and in particular clinical situations. Stroke 2007;38:2612–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
