Molecular pathways: adiponectin and leptin signaling in cancer
- PMID: 23355630
- PMCID: PMC3630242
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0930
Molecular pathways: adiponectin and leptin signaling in cancer
Abstract
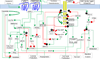
The increasing percentage of obese individuals in the population and its independent association of increased risk for the development of cancer have heightened the necessity to understand the molecular mechanisms that underlie this connection. The deregulation of adipokines in the setting of obesity and their impact on cancer progression and metastasis is one such area of research. Adipokines are bioactive proteins that mediate metabolism, inflammation, angiogenesis, and proliferation. Altered levels of adipokines or their cognate receptors in cancers can ultimately lead to an imbalance in downstream molecular pathways. Discovery of adipokine receptors in various cancers has highlighted the potential for novel therapeutic targets. Leptin and adiponectin represent two adipokines that elicit generally opposing molecular effects. Epidemiologic studies have highlighted associations between increased serum leptin levels and increased tumor growth, whereas adiponectin exhibits an inverse correlation with cancer development. This review addresses the current level of understanding of molecular pathways activated by adiponectin and leptin to identify the areas of intervention and facilitate advancement in the field.
Conflict of interest statement
The author: Michael Nathan VanSaun has disclosed no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bjorbaek C, Kahn BB. Leptin signaling in the central nervous system and the periphery. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004;59:305–331. - PubMed
-
- Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:292–295. - PubMed
-
- Ceddia RB. Direct metabolic regulation in skeletal muscle and fat tissue by leptin: implications for glucose and fatty acids homeostasis. Int J Obes (Lond) 2005;29:1175–1183. - PubMed
-
- St-Pierre J, Tremblay ML. Modulation of leptin resistance by protein tyrosine phosphatases. Cell Metab. 2012;15:292–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

