LIGHT/TNFSR14 can regulate hepatic lipase expression by hepatocytes independent of T cells and Kupffer cells
- PMID: 23355893
- PMCID: PMC3552851
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054719
LIGHT/TNFSR14 can regulate hepatic lipase expression by hepatocytes independent of T cells and Kupffer cells
Abstract
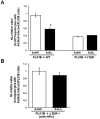
LIGHT/TNFSF14 is a costimulatory molecule expressed on activated T cells for activation and maintenance of T cell homeostasis. LIGHT over expressed in T cells also down regulates hepatic lipase levels in mice through lymphotoxin beta receptor (LTβR) signaling. It is unclear whether LIGHT regulates hepatic lipase directly by interacting with LTβR expressing cells in the liver or indirectly by activation of T cells, and whether Kupffer cells, a major cell populations in the liver that expresses the LTβR, are required. Here we report that LIGHT expression via an adenoviral vector (Ad-LIGHT) is sufficient to down regulate hepatic lipase expression in mice. Depletion of Kupffer cells using clodronate liposomes had no effect on LIGHT-mediated down regulation of hepatic lipase. LIGHT-mediated regulation of hepatic lipase is also independent of LIGHT expression by T cells or activation of T cells. This is demonstrated by the decreased hepatic lipase expression in the liver of Ad-LIGHT infected recombination activating gene deficient mice that lack mature T cells and by the Ad-LIGHT infection of primary hepatocytes. Hepatic lipase expression was not responsive to LIGHT when mice lacking LTβR globally or only on hepatocytes were infected with Ad-LIGHT. Therefore, our data argues that interaction of LIGHT with LTβR on hepatocytes, but not Kupffer cells, is sufficient to down regulate hepatic lipase expression and that this effect can be independent of LIGHT's costimulatory function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
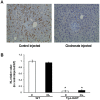
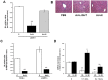
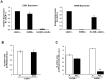
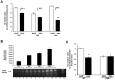
References
-
- Ware CF (2005) Network communications: lymphotoxins, LIGHT, and TNF. Annu Rev Immunol 23: 787–819. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, Tamada K, Chen L (2007) LIGHT-related molecular network in the regulation of innate and adoptive immunity. Immunol Res 37: 17–32. - PubMed
-
- Lee WH, Kim SH, Lee Y, Lee BB, Kwon B, et al. (2001) Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 14 is involved in atherogenesis by inducing proinflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21: 2004–2010. - PubMed
-
- Scholz H, Sandberg W, Damås JK, Smith C, Anreassen AK, et al. (2005) Enhanced plasma levels of LIGHT in unstable angina: possible pathogenic role in foam cell formation and thrombosis. Circulation 112: 2121–2129. - PubMed
