Attractiveness of an aggregation pheromone lure and chicken droppings to adults and larvae of Alphitobius diaperinus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae)
- PMID: 23356087
- PMCID: PMC7109890
- DOI: 10.1603/ec11422
Attractiveness of an aggregation pheromone lure and chicken droppings to adults and larvae of Alphitobius diaperinus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae)
Abstract
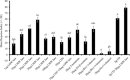
The chemical cues by which lesser mealworm, Alphitobius diaperinus (Panzer) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) beetles find each other are still unknown. Laboratory two-choice pitfall bioassays were conducted to evaluate the attractiveness of synthetic aggregation pheromone lure to lesser mealworm adults and larvae. All components of this synthetic aggregation pheromone lure, including: (R)-(+)-limonene, (E)-beta-ocimene, (S)-(+)-linalool, (R)-(+)-daucene, and 2-nonanone were also tested singly. Chicken dropping volatile compounds and fresh chicken droppings (CD) were evaluated singly or in combination with the pheromone lure. In Arkansas, trapping experiments were conducted in different poultry houses with low, moderate, and high lesser mealworm populations to evaluate the attraction of pheromone lure. Laboratory two-choice pitfall bioassay was found to be a useful and convenient tool for evaluating the attractants before testing them in the poultry house. Greater attraction of adults and larvae to a dose of 20-30 microg pheromone lure was identified in laboratory two-choice pitfall bioassays. Adults and larvae were highly attractive to a combination of fresh CD and pheromone lure, whereas, a combination of chicken dropping volatile and pheromone lure was not significantly attractive. The low attraction of limonene and linalool in the laboratory two-choice pitfall bioassays suggest that either they are nonattractive or attractive only at a narrow range of concentrations. Higher numbers of lesser mealworm adults and larvae were found in traps treated with pheromone lure as compared with untreated controls in field experiments. Results indicate a potential for combining the pheromone lure with the attractive CD compounds to enhance trap efficacy.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham V. A., Faleiro J. R., Al-Shuaibi M. A., Kumar T. P. 2000. A strategy to manage red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Oliv. On date palm Phoenix dactylifera L. Its successful implementation in Al-Hassa, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Pestology 24: 23–30.
-
- Asaniyan E. K., Laseinde E.A.O., Agbede J. O. 2007. Prevalence of darkling beetles (Alphitobius diaperinus) and bacterial load in broiler litters. Intl. J. Poult. Sci. 6: 440–444.
-
- Bartelt R. J., Zilkowski B. W., Cossé A. A., Steelman C. D., Singh N. 2009. Male-produced aggregation pheromone of the lesser mealworm beetle Alphitobius diaperinus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 35: 422–434. - PubMed
-
- Blight M. M., Pickett J. A., Smith M. C., Wadhams L. J. 1984. An aggregation pheromone of Sitona lineatus. Naturwissenschaften 71: 480.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

