Changes in red blood cell membrane structure in type 2 diabetes: a scanning electron and atomic force microscopy study
- PMID: 23356738
- PMCID: PMC3599682
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-12-25
Changes in red blood cell membrane structure in type 2 diabetes: a scanning electron and atomic force microscopy study
Abstract
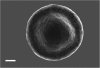
Red blood cells (RBCs) are highly deformable and possess a robust membrane that can withstand shear force. Previous research showed that in diabetic patients, there is a changed RBC ultrastructure, where these cells are elongated and twist around spontaneously formed fibrin fibers. These changes may impact erythrocyte function. Ultrastructural analysis of RBCs in inflammatory and degenerative diseases can no longer be ignored and should form a fundamental research tool in clinical studies. Consequently, we investigated the membrane roughness and ultrastructural changes in type 2 diabetes. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) was used to study membrane roughness and we correlate this with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to compare results of both the techniques with the RBCs of healthy individuals. We show that the combined AFM and SEM analyses of RBCs give valuable information about the disease status of patients with diabetes. Effectiveness of treatment regimes on the integrity, cell shape and roughness of RBCs may be tracked, as this cell's health status is crucial to the overall wellness of the diabetic patient.
Figures

References
-
- Kozlova EK, Chernysh AM, Moroz VV, Kuzovlev AN. Analysis of nanostructure of red blood cells membranes by space Fourier transform of AFM images. Micron. 2012;44:218–227. - PubMed
-
- Girasole M, Pompeo G, Cricenti A, Congiu-Castellano A, Andreola F, Serafino A, Frazer BH, Boumis G, Amiconi G. Roughness of the plasma membrane as an independent morphological parameter to study RBCs: a quantitative atomic force microscopy investigation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1768(5):1268–1276. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.01.014. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

