The clinical and cost-effectiveness of the BRinging Information and Guided Help Together (BRIGHT) intervention for the self-management support of people with stage 3 chronic kidney disease in primary care: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 23356861
- PMCID: PMC3599273
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-14-28
The clinical and cost-effectiveness of the BRinging Information and Guided Help Together (BRIGHT) intervention for the self-management support of people with stage 3 chronic kidney disease in primary care: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Improving the quality of care for people with vascular disease is a key priority. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has recently been included as a target condition for general practices to add to registers of chronic conditions as part of the Quality and Outcome Framework. This paper outlines the implementation and evaluation of a self-management intervention involving an information guidebook, tailored access to local resources and telephone support for people with stage 3 chronic kidney disease.
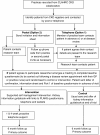
Methods/design: The study involves a multi-site, longitudinal patient-level randomized controlled trial. The study will evaluate the clinical use and cost-effectiveness of a complex self-management intervention for people with stage 3 chronic kidney disease in terms of self-management capacity, health-related quality of life and blood pressure control compared to care as usual. We describe the methods of the patient-level randomized controlled trial.
Discussion: The management of chronic kidney disease is a developing area of research. The BRinging Information and Guided Help Together (BRIGHT) trial aims to provide evidence that a complementary package of support for people with vascular disease that targets both clinical and social need broadens the opportunities of self-management support by addressing problems related to social disadvantage.
Trial registration: Trial registration reference: ISRCTN45433299.
Figures
References
-
- Department of Health. Vascular Disease Briefing Pack. 2009. http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/Publicati....
-
- Rogers A, Kennedy A, Bower P, Gardner C, Gately C, Lee V, Reeves D, Richardson G. The United Kingdom Expert Patients Programme: results and implications from a national evaluation. Med J Australia. 2008;189:S21–S24. - PubMed
-
- Blickem C, Bower P, Protheroe J, Kennedy A, Vassilev I, Sanders C, Kirk S, Chew-Graham C, Rogers A. The role of information in supporting self-care in vascular conditions: a conceptual and empirical review. Health Soc Care Community. 2011;19:449–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2524.2010.00975.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases