Flufenamic acid as an ion channel modulator
- PMID: 23356979
- PMCID: PMC4116821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.01.012
Flufenamic acid as an ion channel modulator
Abstract
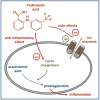
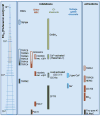
Flufenamic acid has been known since the 1960s to have anti-inflammatory properties attributable to the reduction of prostaglandin synthesis. Thirty years later, flufenamic acid appeared to be an ion channel modulator. Thus, while its use in medicine diminished, its use in ionic channel research expanded. Flufenamic acid commonly not only affects non-selective cation channels and chloride channels, but also modulates potassium, calcium and sodium channels with effective concentrations ranging from 10(-6)M in TRPM4 channel inhibition to 10(-3)M in two-pore outwardly rectifying potassium channel activation. Because flufenamic acid effects develop and reverse rapidly, it is a convenient and widely used tool. However, given the broad spectrum of its targets, experimental results have to be interpreted cautiously. Here we provide an overview of ion channels targeted by flufenamic acid to aid in interpreting its effects at the molecular, cellular, and system levels. If it is used with good practices, flufenamic acid remains a useful tool for ion channel research. Understanding the targets of FFA may help reevaluate its physiological impacts and revive interest in its therapeutic potential.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts if interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aly FA, Al-Tamimi SA, Alwarthan AA. Determination of flufenamic acid and mefenamic acid in pharmaceutical preparations and biological fluids using flow injection analysis with tris(2,2’-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) chemiluminescence detection. Analitica Chmica Acta. 2000;416:87–96.
-
- Baulac S, Huberfeld G, Gourfinkel-An I, Mitropoulou G, Beranger A, Prud’homme JF, Baulac M, Brice A, Bruzzone R, LeGuern E. First genetic evidence of GABA(A) receptor dysfunction in epilepsy: a mutation in the gamma2-subunit gene. Nature genetics. 2001;28:46–48. - PubMed
-
- Baumgarten CM, Clemo HF. Swelling-activated chloride channels in cardiac physiology and pathophysiology. Progress in biophysics and molecular biology. 2003;82:25–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

