Parallel dopamine D1 receptor activity dependence of l-Dopa-induced normal movement and dyskinesia in mice
- PMID: 23357114
- PMCID: PMC3616626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.12.065
Parallel dopamine D1 receptor activity dependence of l-Dopa-induced normal movement and dyskinesia in mice
Abstract
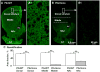
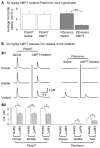
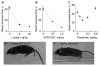
l-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine (l-Dopa)-induced dyskinesia (LID) in Parkinson's disease (PD) is a major clinical problem. The prevailing view is that in PD patients and animal PD models dyskinesia develops after repeated l-dopa use or priming, independent of l-dopa's anti-PD therapeutic effect that occurs immediately. Here we show that in mice with severe and consistent dopamine (DA) loss in the dorsal striatum, rendered by transcription factor Pitx3 null mutation, the very first injection of l-dopa or D1-like agonist SKF81297 induced both normal ambulatory and dyskinetic movements. Furthermore, the robust stimulating effects on normal and dyskinetic movements had an identical time course and parallel dose-response curves. In contrast, D2-like agonist ropinirole stimulated normal and dyskinetic movements relatively modestly. These results demonstrate that severe DA loss in the dorsal striatum sets the stage for dyskinesia to occur on the first exposure to l-dopa or a D1 agonist without any priming. These results also indicate that l-dopa stimulated both normal and dyskinetic movements primarily via D1 receptor activation and that proper D1 agonism is potentially an efficacious therapy for PD motor deficits.
Copyright © 2013 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
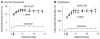

Similar articles
-
MK-801 alters the effects of priming with L-DOPA on dopamine D1 receptor-induced changes in neuropeptide mRNA levels in the rat striatal output neurons.Synapse. 2002 Jan;43(1):1-11. doi: 10.1002/syn.1113. Synapse. 2002. PMID: 11746728
-
L-DOPA Oppositely Regulates Synaptic Strength and Spine Morphology in D1 and D2 Striatal Projection Neurons in Dyskinesia.Cereb Cortex. 2016 Oct 17;26(11):4253-4264. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhw263. Cereb Cortex. 2016. PMID: 27613437 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine receptor cooperativity synergistically drives dyskinesia, motor behavior, and striatal GABA neurotransmission in hemiparkinsonian rats.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Sep 1;174:108138. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108138. Epub 2020 May 31. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32492451
-
Involvement of canonical and non-canonical D1 dopamine receptor signalling pathways in L-dopa-induced dyskinesia.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009 Dec;15 Suppl 3:S64-7. doi: 10.1016/S1353-8020(09)70783-7. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009. PMID: 20083011 Review.
-
mGlu5, Dopamine D2 and Adenosine A2A Receptors in L-DOPA-induced Dyskinesias.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14(5):481-93. doi: 10.2174/1570159x14666151201185652. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26639458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current Knowledge on the Background, Pathophysiology and Treatment of Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia-Literature Review.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 25;10(19):4377. doi: 10.3390/jcm10194377. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34640395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Supersensitive presynaptic dopamine D2 receptor inhibition of the striatopallidal projection in nigrostriatal dopamine-deficient mice.J Neurophysiol. 2013 Nov;110(9):2203-16. doi: 10.1152/jn.00161.2013. Epub 2013 Aug 14. J Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23945778 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine-independent development and maintenance of mouse striatal medium spiny neuron dendritic spines.Neurobiol Dis. 2023 Jun 1;181:106096. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106096. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Neurobiol Dis. 2023. PMID: 37001611 Free PMC article.
-
Striatal But Not Extrastriatal Dopamine Receptors Are Critical to Dopaminergic Motor Stimulation.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Dec 21;8:935. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00935. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29311936 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Synaptic Remodeling by Dopamine in Direct and Indirect Striatal Projection Neurons in Pitx3-/- Mice, a Genetic Model of Parkinson's Disease.J Neurosci. 2018 Apr 11;38(15):3619-3630. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3184-17.2018. Epub 2018 Feb 26. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29483281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlskog JE, Muenter MD. Frequency of levodopa-related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Mov Disord. 2001;16:448–458. - PubMed
-
- Ballard PA, Tetrud JW, Langston JW. Permanent human parkinsonism due to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP): seven cases. Neurology. 1985;35:949–956. - PubMed
-
- Bezard E, Ferry S, Mach U, Stark H, Leriche L, Boraud T, Gross C, Sokoloff P. Attenuation of levodopa-induced dyskinesia by normalizing dopamine D3 receptor function. Nat Med. 2003;9:762–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

