Physical and mental quality of life in chronic pancreatitis: a case-control study from the North American Pancreatitis Study 2 cohort
- PMID: 23357924
- PMCID: PMC3618567
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31826532e7
Physical and mental quality of life in chronic pancreatitis: a case-control study from the North American Pancreatitis Study 2 cohort
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study was to define the quality of life (QOL) in patients with chronic pancreatitis (CP).
Methods: We studied 443 well-phenotyped CP subjects and 611 control subjects prospectively enrolled from 20 US centers between 2000 and 2006 in the North American Pancreatitis Study 2. Responses to the SF-12 questionnaire were used to calculate the mental (MCS) and physical component summary scores (PCS) with norm-based scoring (normal ≥50). Quality of life in CP subjects was compared with control subjects after controlling for demographic factors, drinking history, smoking, and medical conditions. Quality of life in CP was also compared with known scores for several chronic conditions.
Results: Both PCS (38 [SD, 11.5] vs 52 [SD, 9.4]) and MCS (44 [SD, 11.5] vs 51 [SD, 9.2]) were significantly lower in CP compared with control subjects (P < 0.001). On multivariable analyses, compared with control subjects, a profound decrease in physical QOL (PCS 12.02 points lower) and a clinically significant decrease in mental QOL (MCS 4.24 points lower) was seen due to CP. Quality of life in CP was similar to (heart, kidney, liver, lung disease) or worse than (nonskin cancers, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, rheumatoid arthritis) other chronic conditions.
Conclusions: The impact of CP on QOL appears substantial. The QOL in CP subjects appears to be worse or similar to the QOL of many other chronic conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
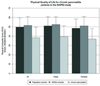




50 year old Caucasian control or chronic pancreatitis patient with BMI of 25 who is a lifetime abstainer, non-smoker and has no history of diabetes, heart attack/stroke or gallstones/gallbladder removal
Subject in A who is also a current smoker
Subject in B who also has diabetes
Subject in C who also has a history of heart attack or stroke and gallstones or gallbladder removal
50 year old Caucasian control or chronic pancreatitis patient with BMI of 25 who is a lifetime abstainer, non-smoker and has no history of diabetes, heart attack/stroke or gallstones/gallbladder removal
Subject in A who is also a current smoker
Subject in B who also has a history of heart attack or stroke
Subject in C who also has a history of diabetes and gallstones or gallbladder removal

50 year old Caucasian control or chronic pancreatitis patient with BMI of 25 who is a lifetime abstainer, non-smoker and has no history of diabetes, heart attack/stroke or gallstones/gallbladder removal
Subject in A who is also a current smoker
Subject in B who also has diabetes
Subject in C who also has a history of heart attack or stroke and gallstones or gallbladder removal
50 year old Caucasian control or chronic pancreatitis patient with BMI of 25 who is a lifetime abstainer, non-smoker and has no history of diabetes, heart attack/stroke or gallstones/gallbladder removal
Subject in A who is also a current smoker
Subject in B who also has a history of heart attack or stroke
Subject in C who also has a history of diabetes and gallstones or gallbladder removal
References
-
- Etemad B, Whitcomb DC. Chronic pancreatitis: diagnosis, classification, and new genetic developments. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:682–707. - PubMed
-
- Ammann RW, Akovbiantz A, Largiader F, et al. Course and outcome of chronic pancreatitis. Longitudinal study of a mixed medical-surgical series of 245 patients. Gastroenterology. 1984;86:820–8282. - PubMed
-
- Steer ML, Waxman I, Freedman S. Chronic pancreatitis. New England Journal of Medicine. 1995;332(22):1482–1490. - PubMed
-
- Witt H, Apte M, Keim V, et al. Chronic pancreatitis: Challenges and advances in pathogenesis, genetics, diagnosis, and therapy. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:1557–1573. - PubMed
-
- Guyatt GH, Feeny DH, Patrick DL. Measuring Health-related Quality of Life. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1993;118:622–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

