PIASγ enhanced SUMO-2 modification of Nurr1 activation-function-1 domain limits Nurr1 transcriptional synergy
- PMID: 23358114
- PMCID: PMC3554661
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055035
PIASγ enhanced SUMO-2 modification of Nurr1 activation-function-1 domain limits Nurr1 transcriptional synergy
Abstract
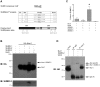
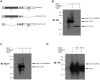
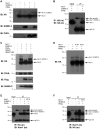
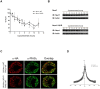
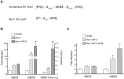
Nurr1 (NR4A2) is a transcription factor that belongs to the orphan NR4A group of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Nurr1 plays key roles in the origin and maintenance of midbrain dopamine neurons, and peripheral inflammatory processes. PIASγ, a SUMO-E3 ligase, represses Nurr1 transcriptional activity. We report that Nurr1 is SUMOylated by SUMO-2 in the lysine 91 located in the transcriptional activation function 1 domain of Nurr1. Nurr1 SUMOylation by SUMO-2 is markedly facilitated by overexpressing wild type PIASγ, but not by a mutant form of PIASγ lacking its first LXXLL motif (PIASγmut1). This PIASγmut1 is also unable to interact with Nurr1 and to repress Nurr1 transcriptional activity. Interestingly, the mutant PIASγC342A that lacks SUMO ligase activity is still able to significantly repress Nurr1-dependent transcriptional activity, but not to enhance Nurr1 SUMOylation. A SUMOylation-deficient Nurr1 mutant displays higher transcriptional activity than the wild type Nurr1 only in promoters harboring more than one Nurr1 response element. Furthermore, lysine 91, the major target of Nurr1 SUMOylation is contained in a canonical synergy control motif, indicating that SUMO-2 posttranslational modification of Nurr1 regulates its transcriptional synergy in complex promoters. In conclusion, PIASγ can exert two types of negative regulations over Nurr1. On one hand, PIASγ limits Nurr1 transactivation in complex promoters by SUMOylating its lysine 91. On the other hand, PIASγ fully represses Nurr1 transactivation through a direct interaction, independently of its E3-ligase activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Perlmann T, Wallén-Mackenzie A (2004) Nurr1, an orphan nuclear receptor with essential functions in developing dopamine cells. Cell Tissue Res 318: 45–52. - PubMed
-
- Maruyama K, Tsukada T, Ohkura N, Bandoh S, Hosono T, et al. (1998) The NGFI-B subfamily of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Int J Oncol 12: 1237–1243. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Benoit G, Liu J, Prasad S, Aarnisalo P, et al. (2003) Structure and function of Nurr1 identifies a class of ligand-independent nuclear receptors. Nature 423: 555–560. - PubMed
-
- Castro DS, Arvidsson M, Bondesson-Bolin M, Perlmann T (1999) Activity of the Nurr1 carboxy-terminal domain depends on cell type and integrity of the activation function 2. J Biol Chem 274: 37483–37490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

