Urinary microRNA profiling in the nephropathy of type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 23358711
- PMCID: PMC3554645
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054662
Urinary microRNA profiling in the nephropathy of type 1 diabetes
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(8). doi:10.1371/annotation/37e647d5-1781-4edf-86a8-e3b533c32ad9
Abstract
Background: Patients with Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) are particularly vulnerable to development of Diabetic nephropathy (DN) leading to End Stage Renal Disease. Hence a better understanding of the factors affecting kidney disease progression in T1D is urgently needed. In recent years microRNAs have emerged as important post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression in many different health conditions. We hypothesized that urinary microRNA profile of patients will differ in the different stages of diabetic renal disease.
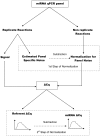
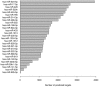
Methods and findings: We studied urine microRNA profiles with qPCR in 40 T1D with >20 year follow up 10 who never developed renal disease (N) matched against 10 patients who went on to develop overt nephropathy (DN), 10 patients with intermittent microalbuminuria (IMA) matched against 10 patients with persistent (PMA) microalbuminuria. A Bayesian procedure was used to normalize and convert raw signals to expression ratios. We applied formal statistical techniques to translate fold changes to profiles of microRNA targets which were then used to make inferences about biological pathways in the Gene Ontology and REACTOME structured vocabularies. A total of 27 microRNAs were found to be present at significantly different levels in different stages of untreated nephropathy. These microRNAs mapped to overlapping pathways pertaining to growth factor signaling and renal fibrosis known to be targeted in diabetic kidney disease.
Conclusions: Urinary microRNA profiles differ across the different stages of diabetic nephropathy. Previous work using experimental, clinical chemistry or biopsy samples has demonstrated differential expression of many of these microRNAs in a variety of chronic renal conditions and diabetes. Combining expression ratios of microRNAs with formal inferences about their predicted mRNA targets and associated biological pathways may yield useful markers for early diagnosis and risk stratification of DN in T1D by inferring the alteration of renal molecular processes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Molitch ME, DeFronzo RA, Franz MJ, Keane WF, Mogensen CE, et al. (2004) Nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care 27 Suppl 1S79–83. - PubMed
-
- Kanwar YS, Sun L, Xie P, Liu F-Y, Chen S (2011) A glimpse of various pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. Annu Rev Pathol 6: 395–423 doi:10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092150. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ (2009) Origins and Mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136: 642–655 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.035. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Ambros V (2001) An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294: 862–864 doi:10.1126/science.1065329. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS, Bartel DP (2010) Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 466: 835–840 doi:10.1038/nature09267. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

