The implication of vitamin D and autoimmunity: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 23359064
- PMCID: PMC6047889
- DOI: 10.1007/s12016-013-8361-3
The implication of vitamin D and autoimmunity: a comprehensive review
Abstract
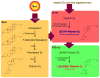
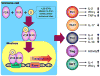
Historically, vitamin D has been associated with the regulation of bone metabolism. However, increasing evidence demonstrates a strong association between vitamin D signaling and many biological processes that regulate immune responses. The discovery of the vitamin D receptor in multiple immune cell lineages, such as monocytes, dendritic cells, and activated T cells credits vitamin D with a novel role in modulating immunological functions and its subsequent role in the development or prevention of autoimmune diseases. In this review we, discuss five major areas in vitamin D biology of high immunological significance: (1) the metabolism of vitamin D; (2) the significance of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms in autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and systemic lupus erythematosus; (3) vitamin D receptor transcriptional regulation of immune cell lineages, including Th1, Th17, Th2, regulatory T, and natural killer T cells; (4) the prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency in patients with multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and systemic lupus erythematosus; and finally, (5) the therapeutic effects of vitamin D supplementation on disease severity and progression.
Figures
References
-
- Holick MF, Chen TC. Vitamin D deficiency: a worldwide problem with health consequences. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87:1080S–1086S. - PubMed
-
- Agmon-Levin N, Kivity S, Tzioufas AG, et al. Low levels of vitamin-D are associated with neuropathy and lymphoma among patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. J Autoimmun. 2012;39:234–239. - PubMed
-
- Giovannucci E, Liu Y, Rimm EB, et al. Prospective study of predictors of vitamin D status and cancer incidence and mortality in men. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:451–459. - PubMed
-
- Giovannucci E. Vitamin D and cancer incidence in the Harvard cohorts. Ann Epidemiol. 2009;19:84–88. - PubMed
-
- Twig G, Shina A, Amital H, Shoenfeld Y. Pathogenesis of infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss in thyroid autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 2012;38:J275–J281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

