Transgenic overexpression of 14-3-3 zeta protects hippocampus against endoplasmic reticulum stress and status epilepticus in vivo
- PMID: 23359526
- PMCID: PMC3554740
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054491
Transgenic overexpression of 14-3-3 zeta protects hippocampus against endoplasmic reticulum stress and status epilepticus in vivo
Abstract
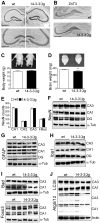
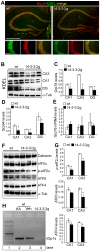
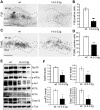
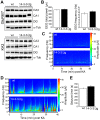
14-3-3 proteins are ubiquitous molecular chaperones that are abundantly expressed in the brain where they regulate cell functions including metabolism, the cell cycle and apoptosis. Brain levels of several 14-3-3 isoforms are altered in diseases of the nervous system, including epilepsy. The 14-3-3 zeta (ζ) isoform has been linked to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) function in neurons, with reduced levels provoking ER stress and increasing vulnerability to excitotoxic injury. Here we report that transgenic overexpression of 14-3-3ζ in mice results in selective changes to the unfolded protein response pathway in the hippocampus, including down-regulation of glucose-regulated proteins 78 and 94, activating transcription factors 4 and 6, and Xbp1 splicing. No differences were found between wild-type mice and transgenic mice for levels of other 14-3-3 isoforms or various other 14-3-3 binding proteins. 14-3-3ζ overexpressing mice were potently protected against cell death caused by intracerebroventricular injection of the ER stressor tunicamycin. 14-3-3ζ overexpressing mice were also potently protected against neuronal death caused by prolonged seizures. These studies demonstrate that increased 14-3-3ζ levels protect against ER stress and seizure-damage despite down-regulation of the unfolded protein response. Delivery of 14-3-3ζ may protect against pathologic changes resulting from prolonged or repeated seizures or where injuries provoke ER stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

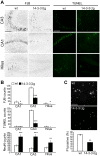
References
-
- van Hemert MJ, Steensma HY, van Heusden GP (2001) 14-3-3 proteins: key regulators of cell division, signalling and apoptosis. Bioessays 23: 936–946. - PubMed
-
- Berg D, Holzmann C, Riess O (2003) 14-3-3 proteins in the nervous system. Nature Rev Neurosci 4: 752–762. - PubMed
-
- Kaneko K, Hachiya NS (2006) The alternative role of 14-3-3 zeta as a sweeper of misfolded proteins in disease conditions. Med Hypotheses 67: 169–171. - PubMed
-
- O’Kelly I, Butler MH, Zilberberg N, Goldstein SA (2002) Forward transport. 14-3-3 binding overcomes retention in endoplasmic reticulum by dibasic signals. Cell 111: 577–588. - PubMed
-
- Toyo-oka K, Shionoya A, Gambello MJ, Cardoso C, Leventer R, et al. (2003) 14-3-3epsilon is important for neuronal migration by binding to NUDEL: a molecular explanation for Miller-Dieker syndrome. Nat Genet 34: 274–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

