Genetic ablation of aquaporin-2 in the mouse connecting tubules results in defective renal water handling
- PMID: 23359673
- PMCID: PMC3634529
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.250852
Genetic ablation of aquaporin-2 in the mouse connecting tubules results in defective renal water handling
Abstract
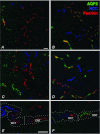
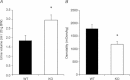
Body water balance is regulated via the water channel aquaporin-2 (AQP2), which is expressed in the renal connecting tubule (CNT) and collecting duct (CD). The relative roles of AQP2 in the CNT and CD are not fully understood. To study the role of AQP2 in the CNT we generated a mouse model with CNT-specific AQP2 deletion (AQP2-CNT-knockout (KO)). Confocal laser scanning microscopy and immunogold electron microscopy demonstrated an absence of AQP2 in the CNT of AQP2-CNT-KO mice. Twenty-four hour urine output was significantly increased (KO: 3.0 ± 0.3 ml (20 g body weight (BW))(-1); wild-type (WT): 1.9 ± 0.3 ml (20 g BW)(-1)) and urine osmolality decreased (KO: 1179 ± 107 mosmol kg(-1); WT: 1790 ± 146 mosmol kg(-1)) in AQP2-CNT-KO mice compared with controls. After 24 h water restriction, urine osmolality was still significantly lower in AQP2-CNT-KO mice (KO: 2087 ± 169 mosmol kg(-1); WT: 2678 ± 144 mosmol kg(-1)). A significant difference in urine osmolality between groups before desmopressin (dDAVP) (KO: 873 ± 129 mosmol kg(-1); WT: 1387 ± 163 mosmol kg(-1)) was not apparent 2 h after injection, with urine osmolality increased significantly in both groups (KO: 2944 ± 41 mosmol kg(-1); WT: 3133 ± 66 mosmol kg(-1)). Cortical kidney fractions from AQP2-CNT-KO mice had significantly reduced AQP2, with no compensatory changes in sodium potassium chloride cotransporter (NKCC2), AQP3 or AQP4. Lithium chloride treatment increased urine volume and decreased osmolality in both WT and AQP2-CNT-KO mice. After 8 days of treatment, the AQP2-CNT-KO mice still had a significantly higher urine volume and lower urine osmolality, suggesting that the CNT does not play a significant role in the pathology of lithium-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Our studies indicate that the CNT plays a role in regulating body water balance under basal conditions, but not for maximal concentration of the urine during antidiuresis.
Figures







References
-
- Bailey MA, Cantone A, Yan Q, MacGregor GG, Leng Q, Amorim JB, Wang T, Hebert SC, Giebisch G, Malnic G. Maxi-K channels contribute to urinary potassium excretion in the ROMK-deficient mouse model of Type II Bartter's syndrome and in adaptation to a high-K diet. Kidney Int. 2006;70:51–59. - PubMed
-
- Boton R, Gaviria M, Batlle DC. Prevalence, pathogenesis, and treatment of renal dysfunction associated with chronic lithium therapy. Am J Kidney Dis. 1987;10:329–345. - PubMed
-
- Christensen BM, Kim YH, Kwon TH, Nielsen S. Lithium treatment induces a marked proliferation of primarily principal cells in rat kidney inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;291:F39–F48. - PubMed
-
- Christensen BM, Marples D, Kim YH, Wang W, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S. Changes in cellular composition of kidney collecting duct cells in rats with lithium-induced NDI. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286:C952–C964. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

