CGAL: computing genome assembly likelihoods
- PMID: 23360652
- PMCID: PMC3663106
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-1-r8
CGAL: computing genome assembly likelihoods
Abstract
Assembly algorithms have been extensively benchmarked using simulated data so that results can be compared to ground truth. However, in de novo assembly, only crude metrics such as contig number and size are typically used to evaluate assembly quality. We present CGAL, a novel likelihood-based approach to assembly assessment in the absence of a ground truth. We show that likelihood is more accurate than other metrics currently used for evaluating assemblies, and describe its application to the optimization and comparison of assembly algorithms. Our methods are implemented in software that is freely available at http://bio.math.berkeley.edu/cgal/.
Figures
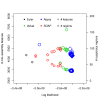
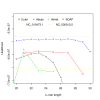
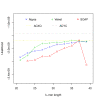
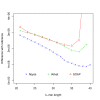

References
-
- Medvedev P, Georgiou K, Myers G, Brudno M. In: Algorithms in Bioinformatics, Volume 4645 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Giancarlo R, Hannenhalli S, editor. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer; 2007. Computability of models for sequence assembly. pp. 289–301.http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74126-8_27 - DOI
-
- Earl DA, Bradnam K, St John J, Darling A, Lin D, Faas J, Yu HOK, Vince B, Zerbino DR, Diekhans M, Nguyen N, Nuwantha P, Sung AWK, Ning Z, Haimel M, Simpson JT, Fronseca NA, Birol N, Docking TR, Ho IY, Rokhsar DS, Chikhi R, Lavenier D, Chapuis G, Naquin D, Maillet N, Schatz MC, Kelly DR, Phillippy AM, Koren S. et al.Assemblathon 1: a competitive assessment of de novo short read assembly methods. Genome Research. 2011;12:2224–2241. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

