The functional maturation of M cells is dramatically reduced in the Peyer's patches of aged mice
- PMID: 23360902
- PMCID: PMC3747980
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2012.141
The functional maturation of M cells is dramatically reduced in the Peyer's patches of aged mice
Abstract
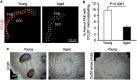
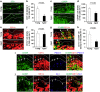
The transcytosis of antigens across the follicle-associated epithelium (FAE) of Peyer's patches by microfold cells (M cells) is important for the induction of efficient immune responses to mucosal antigens. The mucosal immune response is compromised by ageing, but effects on M cells were unknown. We show that M-cell density in the FAE of aged mice was dramatically reduced. As a consequence, aged Peyer's patches were significantly deficient in their ability to transcytose particulate lumenal antigen across the FAE. Ageing specifically impaired the expression of Spi-B and the downstream functional maturation of M cells. Ageing also dramatically impaired C-C motif chemokine ligand 20 expression by the FAE. As a consequence, fewer B cells were attracted towards the FAE, potentially reducing their ability to promote M-cell maturation. Our study demonstrates that ageing dramatically impedes the functional maturation of M cells, revealing an important ageing-related defect in the mucosal immune system's ability to sample lumenal antigens.
Figures
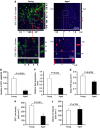

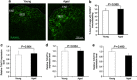
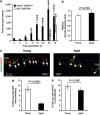
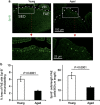
Similar articles
-
c-Rel is dispensable for the differentiation and functional maturation of M cells in the follicle-associated epithelium.Immunobiology. 2017 Feb;222(2):316-326. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2016.09.008. Epub 2016 Sep 18. Immunobiology. 2017. PMID: 27663963 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of claudin expression in follicle-associated epithelium of Peyer's patches: preferential localization of claudin-4 at the apex of the dome region.Lab Invest. 2003 Jul;83(7):1045-53. doi: 10.1097/01.lab.0000078741.55670.6e. Lab Invest. 2003. PMID: 12861044
-
Peptidoglycan recognition protein expression in mouse Peyer's Patch follicle associated epithelium suggests functional specialization.Cell Immunol. 2003 Jul;224(1):8-16. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(03)00155-2. Cell Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14572796
-
Development of Peyer's patches, follicle-associated epithelium and M cell: lessons from immunodeficient and knockout mice.Semin Immunol. 1999 Jun;11(3):183-91. doi: 10.1006/smim.1999.0174. Semin Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10381864 Review.
-
Microfold (M) cells: important immunosurveillance posts in the intestinal epithelium.Mucosal Immunol. 2013 Jul;6(4):666-77. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.30. Epub 2013 May 22. Mucosal Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23695511 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rejuvenation of mucosal immunosenescence by adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Int Immunol. 2017 Jan 1;29(1):5-10. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxx001. Int Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28391291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of co-infection with a small intestine-restricted helminth pathogen on oral prion disease pathogenesis in mice.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 30;9(1):6674. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42900-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31040320 Free PMC article.
-
Gut-Innervating Nociceptor Neurons Regulate Peyer's Patch Microfold Cells and SFB Levels to Mediate Salmonella Host Defense.Cell. 2020 Jan 9;180(1):33-49.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.014. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Cell. 2020. PMID: 31813624 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying human and murine M cells in vitro.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019 May;244(7):554-564. doi: 10.1177/1535370219838674. Epub 2019 Mar 24. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019. PMID: 30907132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging-Related Impairments to M Cells in Peyer's Patches Coincide With Disturbances to Paneth Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 6;12:761949. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.761949. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34938288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krahenbuhl J.P., Neutra M.R. Epithelial M cells: differentiation and function. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2000;16:301–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/D/20251967/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/D/20251968/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F019726/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J0004332/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/J014672/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

