Src activation by β-adrenoreceptors is a key switch for tumour metastasis
- PMID: 23360994
- PMCID: PMC3561638
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2413
Src activation by β-adrenoreceptors is a key switch for tumour metastasis
Erratum in
- Nat Commun. 2013;4:1932. Shazhad, Mian M K [corrected to Shahzad, Mian M K]
Abstract
Noradrenaline can modulate multiple cellular functions important for cancer progression; however, how this single extracellular signal regulates such a broad array of cellular processes is unknown. Here we identify Src as a key regulator of phosphoproteomic signalling networks activated in response to beta-adrenergic signalling in cancer cells. These results also identify a new mechanism of Src phosphorylation that mediates beta-adrenergic/PKA regulation of downstream networks, thereby enhancing tumour cell migration, invasion and growth. In human ovarian cancer samples, high tumoural noradrenaline levels were correlated with high pSrc(Y419) levels. Moreover, among cancer patients, the use of beta blockers was significantly associated with reduced cancer-related mortality. Collectively, these data provide a pivotal molecular target for disrupting neural signalling in the tumour microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
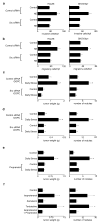
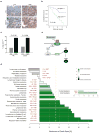
References
-
- Thaker PH, et al. Chronic stress promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma. Nature medicine. 2006;12:939–944. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HV-10-05_(2)/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA96300/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA098258/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA104825/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA096300/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA126474/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA083639/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA128797/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA083639/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140933/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA140933/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA96297/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA101642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA109298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA128797/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA098258/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA140388/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA096297/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31CA126474/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- SC3 GM095417/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA109298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2GM092599/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA151668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA110793/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 GM092599/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA151668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA110793/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA104825/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

