A novel fluorescent lipid probe for dry eye: retrieval by tear lipocalin in humans
- PMID: 23361507
- PMCID: PMC3597195
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.12-10817
A novel fluorescent lipid probe for dry eye: retrieval by tear lipocalin in humans
Abstract
Purpose: A fluorescent probe was used to identify mucin-depleted areas on the ocular surface and to test the hypothesis that tear lipocalin retrieves lipids from the eyes of normal and dry eye subjects.
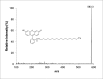
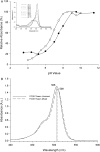
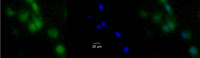
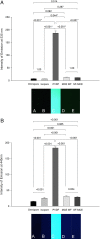
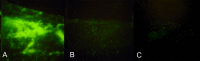
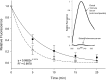
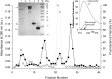
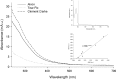
Methods: Fluorescein-labeled octadecyl ester, FODE, was characterized by mass spectrometry and absorbance spectrophotometry. The use of FODE to define mucin defects was studied with impression membranes under conditions that selectively deplete mucin. The kinetics of FODE removal from the ocular surface were analyzed by sampling tears from control and dry eye patients at various times. The tear protein-FODE complexes were isolated by gel filtration and ion exchange chromatographies, monitored with absorption and fluorescent spectroscopies, and analyzed by gel electrophoresis. Immunoprecipitation verified FODE complexed to tear lipocalin in tears.
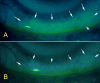
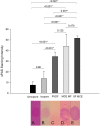
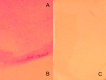
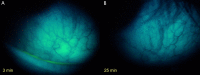
Results: FODE exhibits an isosbestic point at 473 nm, pKa of 7.5, and red shift relative to fluorescein. The low solubility of FODE in buffer is enhanced with 1% Tween 80 and ethanol. FODE adheres to the ocular surface of dry eye patients. FODE produces visible staining at the contact sites of membranes, which correlates with removal of mucin. Despite the fact that tear lipocalin is reduced in dry eye patients, FODE removal follows similar rapid exponential decay functions for all subjects. FODE is bound to tear lipocalin in tears.
Conclusions: Tear lipocalin retrieves lipid rapidly from the human ocular surface in mild to moderate dry eye disease and controls. With improvements in solubility, FODE may have potential as a fluorescent probe to identify mucin-depleted areas.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures
References
-
- Gipson IK. Distribution of mucins at the ocular surface. Exp Eye Res. 2004; 78: 379–388 - PubMed
-
- Gipson IK, Argueso P. Role of mucins in the function of the corneal and conjunctival epithelia. Int Rev Cytol. 2003; 231: 1–49 - PubMed
-
- Gipson IK, Inatomi T. Cellular origin of mucins of the ocular surface tear film. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998; 438: 221–227 - PubMed
-
- Argueso P, Gipson IK. Epithelial mucins of the ocular surface: structure, biosynthesis and function. Exp Eye Res. 2001; 73: 281–289 - PubMed
-
- Argueso P, Spurr-Michaud S, Russo CL, Tisdale A, Gipson IK. MUC16 mucin is expressed by the human ocular surface epithelia and carries the H185 carbohydrate epitope. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44: 2487–2495 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

