Clinical and molecular characterisation of hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia in infants born small-for-gestational age
- PMID: 23362136
- PMCID: PMC3686249
- DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2012-302880
Clinical and molecular characterisation of hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia in infants born small-for-gestational age
Abstract
Objective: To characterise the phenotype and genotype of neonates born small-for-gestational age (SGA; birth weight <10th centile) who developed hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia (HH).
Methods: Clinical information was prospectively collected on 27 SGA neonates with HH, followed by sequencing of KCNJ11 and ABCC8.
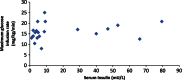
Results: There was no correlation between the maximum glucose requirement and serum insulin levels. Serum insulin level was undetectable in five infants (19%) during hypoglycaemia. Six infants (22%) required diazoxide treatment >6 months. Normoglycaemia on diazoxide <5 mg/kg/day was a safe predictor of resolved HH. Sequencing of KCNJ11/ABCC8 did not identify any mutations.
Conclusions: Serum insulin levels during hypoglycaemia taken in isolation can miss the diagnosis of HH. SGA infants may continue to have hypofattyacidaemic hypoketotic HH beyond the first few weeks of life. Recognition and treatment of this group of patients are important and may have important implications for neurodevelopmental outcome of these patients.
Keywords: Hyperinsulinism; Hypoglycaemia; Small for Gestational Age Infant.
Figures
References
-
- Kapoor RR, Flanagan SE, James C, et al. Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia. Arch Dis Child 2009;94:450–7 - PubMed
-
- Collins JE, Leonard JV. Hyperinsulinism in asphyxiated and small-for-dates infants with hypoglycaemia . Lancet 1984;2:311–13 - PubMed
-
- Hoe FM, Thornton PS, Wanner LA, et al. Clinical features and insulin regulation in infants with a syndrome of prolonged neonatal hyperinsulinism. J Pediatr 2006;148:207–12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical