Thioredoxin-related protein 32 (TRP32) specifically reduces oxidized phosphatase of regenerating liver (PRL)
- PMID: 23362275
- PMCID: PMC3591634
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.418004
Thioredoxin-related protein 32 (TRP32) specifically reduces oxidized phosphatase of regenerating liver (PRL)
Abstract
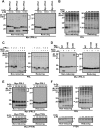
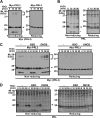
PRL family constitutes a unique class of phosphatases associated with metastasis. The phosphatase activity of PRL has been reported to be important for promoting metastasis, and it is inactivated by reversible oxidation of its catalytic cysteine. Here, we show that TRP32 specifically reduces PRL. Reduction of oxidized PRL in cells is inhibited by 2,4-dinitro-1-chlorobenzene, an inhibitor of TRX reductase. In vitro assays for the reduction of PRL show that only TRP32 can potently reduce oxidized PRL, whereas other TRX-related proteins linked to TRX reductase show little or no reducing activity. Indeed, TRP32 knockdown significantly prolongs the H2O2-induced oxidation of PRL. Binding analyses reveal that the unique C-terminal domain of TRP32 is required and sufficient for its direct interaction with PRL. These results suggest that TRP32 maintains the reduced state of PRL and thus regulates the biological function of PRL.
Figures



References
-
- Cates C. A., Michael R. L., Stayrook K. R., Harvey K. A., Burke Y. D., Randall S. K., Crowell P. L., Crowell D. N. (1996) Prenylation of oncogenic human PTP(CAAX) protein tyrosine phosphatases. Cancer Lett. 110, 49–55 - PubMed
-
- Rios P., Li X., Köhn M. (2013) Molecular mechanisms of the PRL phosphatases. FEBS J. 280, 505–524 - PubMed
-
- Bessette D. C., Qiu D., Pallen C. J. (2008) PRL PTPs: mediators and markers of cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27, 231–252 - PubMed
-
- Zeng Q., Dong J. M., Guo K., Li J., Tan H. X., Koh V., Pallen C. J., Manser E., Hong W. (2003) PRL-3 and PRL-1 promote cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cancer Res. 63, 2716–2722 - PubMed
-
- Al-Aidaroos A. Q., Zeng Q. (2010) PRL-3 phosphatase and cancer metastasis. J. Cell Biochem. 111, 1087–1098 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

