Indications, outcomes, and complications of pedicled propeller perforator flaps for upper body defects: a systematic review
- PMID: 23362479
- PMCID: PMC3556533
- DOI: 10.5999/aps.2013.40.1.44
Indications, outcomes, and complications of pedicled propeller perforator flaps for upper body defects: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: The aim of this investigation was to systematically review the current literature to provide the best data for indications, outcomes, survival, and complication rates of pedicled propeller perforator flaps for upper body defects.
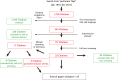
Methods: A comprehensive literature review for articles published from January 1991 to December 2011 was performed using the PubMed, Medline, and Cochrane Databases. Articles without available full-text, single case reports or papers with excessive missing data were excluded. Papers reporting pedicle-perforator (propeller) flaps used for lower extremity reconstruction were excluded from meta-analysis.
Results: From the initial 1,736 studies our search yielded, 343 studies qualified for the second stage of selection. Of 117 full-text reports screened, 41 studies, met the definitive inclusion and exclusion criteria. Of the selected 41 articles, 26 were case series, original papers or retrospective reviews and were included, whereas 15 were case report papers and therefore were excluded. Two hundred ninety-five propeller flaps were reported to have been used in a total of 283 patients. Indications include repair of trauma-induced injuries, post-trauma revision surgery, cancer resection, chronic infection, pressure sores, and chronic ulcers with a major complication rate (3.3%) comparable to that of free flaps. No specific exclusion criteria for the procedure were presented in the studies reviewed.
Conclusions: Pedicled propeller flaps are a versatile and safe reconstructive option that are easy and quick to raise and that provide unlimited clinical solutions because of the theoretical possibility of harvesting them based on any perforator chosen among those classified in the body.
Keywords: Pedicled flap; Review literature; Surgical flaps.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
-
- Karsidag S, Ozcan A, Sumer O, et al. Single-stage ala nasi reconstruction: lateral nasal artery perforator flap. J Craniofac Surg. 2010;21:1887–1889. - PubMed
-
- Lecours C, Saint-Cyr M, Wong C, et al. Freestyle pedicle perforator flaps: clinical results and vascular anatomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126:1589–1603. - PubMed
-
- D'Arpa S, Cordova A, Pignatti M, et al. Freestyle pedicled perforator flaps: safety, prevention of complications, and management based on 85 consecutive cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128:892–906. - PubMed
-
- Schonauer F, Vuppalapati G, Marlino S, et al. Versatility of the posterior auricular flap in partial ear reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126:1213–1221. - PubMed
-
- Hyakusoku H, Iwakiri I, Murakami M, et al. Central axis flap methods. Burns. 2006;32:891–896. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous