The etiology of treatment-related lymphopenia in patients with malignant gliomas: modeling radiation dose to circulating lymphocytes explains clinical observations and suggests methods of modifying the impact of radiation on immune cells
- PMID: 23362951
- PMCID: PMC3991115
- DOI: 10.3109/07357907.2012.762780
The etiology of treatment-related lymphopenia in patients with malignant gliomas: modeling radiation dose to circulating lymphocytes explains clinical observations and suggests methods of modifying the impact of radiation on immune cells
Abstract
Purpose: Severe treatment-related lymphopenia (TRL) occurs in 40% of patients with high grade gliomas (HGG) receiving glucocorticoids, temozolomide, and radiation. This occurs following radiation, persists for months, and is associated with reduced survival. As all three treatment modalities are lymphotoxic, this study was conducted to estimate the radiation dose that lymphocytes receive passing through the radiation field and if this could explain the observed TRL.
Materials and methods: A typical glioblastoma plan (8-cm tumor, 60 Gy/30 fractions) was constructed using the Pinnacle™ radiation planning system. Radiation doses to circulating cells (DCC) were analyzed using MatLab™. The primary endpoints were mean DCC and percent of circulating cells receiving ≥0.5 Gy. The model was also used to study how changes in target volumes (PTV), dose rates, and delivery techniques affect DCC.
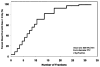
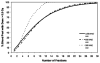
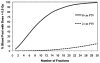
Results: The modeling determined that while a single radiation fraction delivered 0.5 Gy to 5% of circulating cells, after 30 fractions 99% of circulating blood had received ≥0.5 Gy. The mean DCC was 2.2 Gy and was similar for IMRT, 3D-conformal techniques, and different dose rates. Major changes in PTV size affected mean DCC and percent of circulating cells receiving ≥0.5 Gy.
Conclusions: Standard treatment plans for brain tumors deliver potentially lymphotoxic radiation doses to the entire circulating blood pool. Altering dose rates or delivery techniques are unlikely to significantly affect DCC by the end of treatment. Novel approaches are needed to limit radiation to circulating lymphocytes given the association of lymphopenia with poorer survival in patients with HGG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Figures
References
-
- Mahindra AK, Grossman SA. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in HIV negative patients with primary brain tumors. J Neurooncol. 2003;63(3):263–270. - PubMed
-
- Balmanoukian A, Ye X, Herman J, Laheru D, Grossman S. Effect of treatment-related lymphopenia on survival in newly diagnosed patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Clin Invest. 2012 In press.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
