Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an emerging threat to obese and diabetic individuals
- PMID: 23363012
- PMCID: PMC3646408
- DOI: 10.1111/nyas.12016
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an emerging threat to obese and diabetic individuals
Abstract
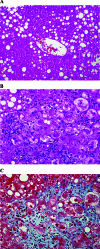
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease in the Western world and its incidence is increasing rapidly. NAFLD is a spectrum ranging from simple steatosis, which is relatively benign hepatically, to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to cirrhosis. Obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and dyslipidemia are the most important risk factors for NAFLD. Due to heavy enrichment with metabolic risk factors, individuals with NAFLD are at significantly higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Individuals with NAFLD have higher incidence of type 2 diabetes. The diagnosis of NAFLD requires imaging evidence of hepatic steatosis in the absence of competing etiologies including significant alcohol consumption. Liver biopsy remains the gold standard for diagnosing NASH and for determining prognosis. Weight loss remains a cornerstone of treatment. Weight loss of ~5% is believed to improve steatosis, whereas ~10% weight loss is necessary to improve steatohepatitis. A number of pharmacologic therapies have been investigated to treat NASH, and agents such as vitamin E and thiazolidinediones have shown promise in select patient subgroups.
© 2013 New York Academy of Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Ekstedt M, Franzen LE, Mathiesen UL, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Hepatology. 2006;44:865–873. - PubMed
-
- Ratziu V, Poynard T. Assessing the outcome of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis? It's time to get serious. Hepatology. 2006;44:802–805. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell SH, Oelsner DH, Iezzoni JC, et al. Cryptogenic cirrhosis: clinical characterization and risk factors for underlying disease. Hepatology. 1999;29:664–669. - PubMed
-
- Charlton M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review of current understanding and future impact. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004;2:1048–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

