Open bite treatment using clear aligners
- PMID: 23363479
- PMCID: PMC8744524
- DOI: 10.2319/080212-627.1
Open bite treatment using clear aligners
Abstract
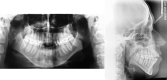
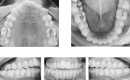
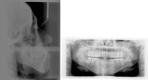
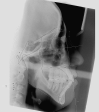
A 35-year-old female patient with dentoalveolar open bite of 4 mm, molar Class I malocclusion, centered midlines, moderate crowding, and labial inclination of the lower incisor was treated with clear aligners to reduce protrusion and close the anterior open bite. The result showed that clear aligners were an effective method with which to correct this malocclusion. The treatment was complete after 18 months. The patient was satisfied with her new appearance and function.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of Clear Aligners in Treating Patients with Anterior Open Bite: A Retrospective Analysis.J Clin Orthod. 2017 Aug;51(8):454-460. J Clin Orthod. 2017. PMID: 29112503 No abstract available.
-
Simplifying the approach of open bite treatment with aligners and selective micro-osteoperforations: An adult case report.Int Orthod. 2021 Mar;19(1):159-169. doi: 10.1016/j.ortho.2020.11.005. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Int Orthod. 2021. PMID: 33358878
-
Chin remodeling in a patient with bimaxillary protrusion and open bite by using mini-implants for temporary anchorage.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2018 Mar;153(3):436-444. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2016.12.030. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2018. PMID: 29501119
-
Lingual treatment of an adult patient with an iatrogenic class II anterior open bite: Report of a case with a non-surgical orthodontic approach.Int Orthod. 2021 Mar;19(1):170-181. doi: 10.1016/j.ortho.2021.01.006. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Int Orthod. 2021. PMID: 33573882
-
Orthodontic treatment of anterior open bite: a review article--is surgery always necessary?Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014 Sep;18(3):271-7. doi: 10.1007/s10006-013-0430-5. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014. PMID: 23949448 Review.
Cited by
-
Class III malocclusion and bilateral cross-bite in an adult patient treated with miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expander and aligners.Angle Orthod. 2018 Sep;88(5):649-664. doi: 10.2319/111617-790.1. Epub 2018 May 1. Angle Orthod. 2018. PMID: 29714067 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of anterior open bites using non-extraction clear aligner therapy in adult patients.Korean J Orthod. 2022 May 25;52(3):210-219. doi: 10.4041/kjod21.180. Korean J Orthod. 2022. PMID: 35527369 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis on the Impact of Various Aligner Materials and Attachments on Orthodontic Tooth Movement.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Apr 10;14(4):209. doi: 10.3390/jfb14040209. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37103299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correction of anterior open bite of varying severity using clear aligner therapy-A case series.Clin Case Rep. 2022 Aug 29;10(8):e6277. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.6277. eCollection 2022 Aug. Clin Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36052021 Free PMC article.
-
Cone beam computed tomography analysis of anterior open bite management using clear aligners: a single-arm retrospective study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 11;15(1):25145. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09157-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40646026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Subtelny JD, Sakuda M. Openbite diagnosis and treatment. Am J Orthod. 1964;50:337–358.
-
- Nahoum HI, Horowitz SL, Benedicto EA. Varieties of anterior open bite. Am J Orthod. 1972;61:486–492. - PubMed
-
- Fujiki T, Inoue M, Miyawaki S, Nagasaki T, Tanamoto K, Takano-Yamamoto T. Relationship between maxillo-facial morphology and deglutive tongue movement in patients with anterior open bite. Am J Orthod. 2004;125:160–167. - PubMed
-
- Nahoum H. Vertical proportions and the palatal plane in anterior open bite. Am J Orthod. 1971;59:273–282. - PubMed
-
- Salzman JA. Radiographic Cephalometrics in Diagnosis and Treatment in Orthodontics in Daily Practice. Philadelphia, Pa: JB Lippincott; 1974. pp. 183–196.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

