A cross sectional study of HPV type prevalence according to age and cytology
- PMID: 23363541
- PMCID: PMC3575232
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-53
A cross sectional study of HPV type prevalence according to age and cytology
Abstract
Background: A cross sectional study to investigate HPV prevalence according to age and cytology.
Methods: Women presenting to a gynaecological outpatient clinic for a Pap smear test were included in the study (n=3177). All women had cervical cytology and HPV testing.
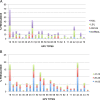
Results: Overall prevalence of any 24 HPV type analysed was 33.1% (95% CI 31.5% to 34.7%) and HPV 16 and HPV 42 were the most frequent (6.7% (95% CI 5.8% to 7.6%), 6.8% (95% CI 5.9% to 7.6%)), in total samples. Multiple HPV infection rate was 12.9% (95% CI 11.8% to 14.1%). High risk HPV (hrHPV) types were present in 27.4% (95% CI 25.8% to 28.9%) of the samples.HPV prevalence was highest among 14 to 19 y.o (46.6% (95% CI 40.7%-52.4%)) and second highest among 30-34 y.o. (39.7%, 95% CI 35.4%-44%). HPV 16 was highest among 20-24 (9.0% (95% CI 6.4%-11.6%)) and second highest among 50 to 54 y.o. (6.3% (95% CI 2.9% to 9.8%).In Low-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (LgSIL) cytology samples, the most frequently detected hrHPV types were: 16 (14.5% (95% CI 12.1% to 16.9%)), 51 (13.0% (95% CI 10.7% to 15.3%)) and 53 (9.1% (95% CI 7.2% to 11.1%)) and in High-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions (HgSIL) were: HPV 16 (37.2% (95% CI 26.5% to 47.9%)), HPV 51 (17.9% (95% CI 9.4% to 26.5%)) and HPV 18 (12.8% (95% CI 5.4% to 20.2%)).
Conclusions: In the population studied, HPV 16 and 51 were the most frequent detected hrHPV types. HPV positivity, hrHPV and multiple HPV types infections were higher in young women, while HPV prevalence declined with increasing age and presented two peaks a higher (14-19 y.o.) and a lower one (30-34 y.o.) These results may contribute to the creation of a national screening programme.
Figures
References
-
- de Sanjose S, Quint WG, Alemany L, Geraets DT, Klaustermeier JE, Lloveras B, Tous S, Felix A, Bravo LE, Shin HR, Vallejos CS, de Ruiz PA, Lima MA, Guimera N, Clavero O, Alejo M, Llombart-Bosch A, Cheng-Yang C, Tatti SA, Kasamatsu E, Iljazovic E, Odida M, Prado R, Seoud M, Grce M, Usubutun A, Jain A, Suarez GA, Lombardi LE, Banjo A. et al. Human papillomavirus genotype attribution in invasive cervical cancer: a retrospective cross-sectional worldwide study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(11):1048–1056. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70230-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clifford GM, Rana RK, Franceschi S, Smith JS, Gough G, Pimenta JM. Human papillomavirus genotype distribution in low-grade cervical lesions: comparison by geographic region and with cervical cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005;14(5):1157–1164. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-04-0812. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smith JS, Melendy A, Rana RK, Pimenta JM. Age-specific prevalence of infection with human papillomavirus in females: a global review. J Adolesc Health. 2008;43(4 Suppl):5–25. S25.e1-41. - PubMed
-
- Muñoz N, Bosch FX, de Sanjose S, Herrero R, Castellsagué X, Shah KV, Snijders PJ, Meijer CJ. International Agency for Research on Cancer Multicenter Cervical Cancer Study Group. Epidemiologic classification of human papillomavirus types associated with cervical cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(6):518–527. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021641. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials