Intermediate filament-associated cytolinker plectin 1c destabilizes microtubules in keratinocytes
- PMID: 23363598
- PMCID: PMC3596248
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-06-0488
Intermediate filament-associated cytolinker plectin 1c destabilizes microtubules in keratinocytes
Abstract
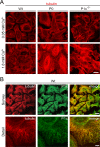
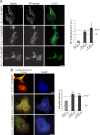
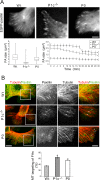
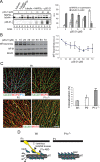
The transition of microtubules (MTs) from an assembled to a disassembled state plays an essential role in several cellular functions. While MT dynamics are often linked to those of actin filaments, little is known about whether intermediate filaments (IFs) have an influence on MT dynamics. We show here that plectin 1c (P1c), one of the multiple isoforms of the IF-associated cytolinker protein plectin, acts as an MT destabilizer. We found that MTs in P1c-deficient (P1c(-/-)) keratinocytes are more resistant toward nocodazole-induced disassembly and display increased acetylation. In addition, live imaging of MTs in P1c(-/-), as well as in plectin-null, cells revealed decreased MT dynamics. Increased MT stability due to P1c deficiency led to changes in cell shape, increased velocity but loss of directionality of migration, smaller-sized focal adhesions, higher glucose uptake, and mitotic spindle aberrations combined with reduced growth rates of cells. On the basis of ex vivo and in vitro experimental approaches, we suggest a mechanism for MT destabilization in which isoform-specific binding of P1c to MTs antagonizes the MT-stabilizing and assembly-promoting function of MT-associated proteins through an inhibitory function exerted by plectin's SH3 domain. Our results open new perspectives on cytolinker-coordinated IF-MT interaction and its physiological significance.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Plectin dysfunction in neurons leads to tau accumulation on microtubules affecting neuritogenesis, organelle trafficking, pain sensitivity and memory.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2021 Feb;47(1):73-95. doi: 10.1111/nan.12635. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 32484610 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-dependent linkage, assembly inhibition and disassembly of vimentin and cytokeratin 5/14 filaments through plectin's intermediate filament-binding domain.J Cell Sci. 2000 Feb;113 ( Pt 3):483-91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.3.483. J Cell Sci. 2000. PMID: 10639335
-
Plectin-controlled keratin cytoarchitecture affects MAP kinases involved in cellular stress response and migration.J Cell Biol. 2006 Aug 14;174(4):557-68. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200605172. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16908671 Free PMC article.
-
Plectin-Mediated Intermediate Filament Functions: Why Isoforms Matter.Cells. 2021 Aug 21;10(8):2154. doi: 10.3390/cells10082154. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plectin-intermediate filament partnership in skin, skeletal muscle, and peripheral nerve.Histochem Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;140(1):33-53. doi: 10.1007/s00418-013-1102-0. Epub 2013 Jun 9. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23748243 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Biology and Clinical Mitigation of Cancer Treatment-Induced Neuropathy.Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2016 Apr 3;10:27-34. doi: 10.4137/CMO.S32810. eCollection 2016. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27081324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Networking galore: intermediate filaments and cell migration.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;25(5):600-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jul 22. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23886476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Diversity of Intermediate Filaments in Astrocytes.Cells. 2020 Jul 2;9(7):1604. doi: 10.3390/cells9071604. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32630739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The plakin domain of C. elegans VAB-10/plectin acts as a hub in a mechanotransduction pathway to promote morphogenesis.Development. 2019 Dec 13;146(24):dev183780. doi: 10.1242/dev.183780. Development. 2019. PMID: 31784459 Free PMC article.
-
Functionally specific binding regions of microtubule-associated protein 2c exhibit distinct conformations and dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 24;293(34):13297-13309. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.001769. Epub 2018 Jun 20. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29925592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackerl R, Walko G, Fuchs P, Fischer I, Schmuth M, Wiche G. Conditional targeting of plectin in prenatal and adult mouse stratified epithelia causes keratinocyte fragility and lesional epidermal barrier defects. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:2435–2443. - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO. Tracking the ends: a dynamic protein network controls the fate of microtubule tips. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:309–322. - PubMed
-
- Andrä K, Kornacker I, Jörgl A, Zörer M, Spazierer D, Fuchs P, Fischer I, Wiche G. Plectin-isoform-specific rescue of hemidesmosomal defects in plectin (–/–) keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2003;120:189–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

