Risk factors for adverse reactions from contrast agents for computed tomography
- PMID: 23363607
- PMCID: PMC3562527
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6947-13-18
Risk factors for adverse reactions from contrast agents for computed tomography
Abstract
Background: Symptoms of an adverse reaction to contrast agents for computed tomography are diverse ranging, and sometimes serious. The goal of this study is to create a scoring rule to predict adverse reactions to contrast agents used in computed tomography.
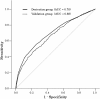
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study of all adult patients undergoing contrast enhanced CT scan for 7 years. The subjects were randomly divided into either a derivation or validation group. Baseline data and clinically relevant factors were collected from the electronic chart. Primary outcome was any acute adverse reactions to contrast media, observed for during 24 hours after administration. All potential candidate predictors were included in a forward stepwise logistic regression model. Prediction scores were assigned based on β coefficient. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was drawn, and the area under the curve (AUC) and incidence of acute adverse reactions at each point were obtained. The same process was performed in the validation group.
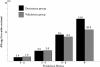
Results: 36,472 patients underwent enhanced CT imaging: 20,000 patients in the derivation group and 16,472 in the validation group. A total of 409 (2.0%, 95% CI:1.9-2.3) and 347 (2.1%, 95% CI:1.9-2.3) acute adverse reactions were seen in the derivation and validation groups. Logistic regression analysis revealed that prior adverse reaction to contrast agents, urticaria, an allergic history to drugs other than contrast agents, contrast agent concentration >70%, age <50 years, and total contrast agent dose >65 g were significant predictors of an acute adverse reaction. AUC was 0.70 (95% CI:0.67-0.73) and 0.67 (95% CI:0.64-0.70) in the derivation and validation groups.
Conclusions: We suggest a prediction model consisting of six predictors for acute adverse reactions to contrast agents used in CT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A prediction rule for the development of delirium among patients in medical wards: Chi-Square Automatic Interaction Detector (CHAID) decision tree analysis model.Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013 Oct;21(10):957-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2012.08.009. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23567433
-
Development and validation of a novel predictive scoring model for microvascular invasion in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Radiol. 2017 Mar;88:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.12.030. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Eur J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28189206
-
Acute Adverse Reactions to Nonionic Iodinated Contrast Media for CT: Prospective Randomized Evaluation of the Effects of Dehydration, Oral Rehydration, and Patient Risk Factors.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016 Nov;207(5):931-938. doi: 10.2214/AJR.16.16051. Epub 2016 Aug 17. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016. PMID: 27533472 Clinical Trial.
-
Venous Thrombosis Risk after Cast Immobilization of the Lower Extremity: Derivation and Validation of a Clinical Prediction Score, L-TRiP(cast), in Three Population-Based Case-Control Studies.PLoS Med. 2015 Nov 10;12(11):e1001899; discussion e1001899. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001899. eCollection 2015 Nov. PLoS Med. 2015. PMID: 26554832 Free PMC article.
-
Visceral adiposity and inflammatory bowel disease.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021 Nov;36(11):2305-2319. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-03968-w. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021. PMID: 34104989 Review.
Cited by
-
Bridging the gap between bench and clinic: the importance of understanding the mechanism of iodinated contrast media hypersensitivity.Br J Radiol. 2023 Jan 1;96(1141):20220494. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20220494. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Br J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36395475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact on liver position under breath-hold by computed tomography contrast agents in stereotactic body radiotherapy of liver cancer.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2021 Dec 30;26(6):1035-1044. doi: 10.5603/RPOR.a2021.0131. eCollection 2021. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2021. PMID: 34992878 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Angiography Shows Increased Arterial Blood Supply Associated with Murine Mammary Cancer.Int J Biomed Imaging. 2019 Jan 17;2019:5987425. doi: 10.1155/2019/5987425. eCollection 2019. Int J Biomed Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30792738 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Adrenal Vein Sampling Using Dexamethasone Premedication in Patients With Iodine Contrast Media Allergy.J Endocr Soc. 2022 Jun 16;6(8):bvac093. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvac093. eCollection 2022 Aug 1. J Endocr Soc. 2022. PMID: 35795806 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenal Vein Sampling in a Patient With Primary Hyperaldosteronism and Severe Contrast Allergy.J Endocr Soc. 2021 Jul 12;5(10):bvab122. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvab122. eCollection 2021 Oct 1. J Endocr Soc. 2021. PMID: 34350369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishizawa KMM, Maruyama T. et al.Survey of CT Practice in Japan and Collective Effective Dose Estimation. Jpn J Radiol. 2004;64:151–158. - PubMed
-
- Brenner D, Elliston C, Hall E, Berdon W. Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from pediatric CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176:289–296. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical