Histone demethylase dUTX antagonizes JAK-STAT signaling to maintain proper gene expression and architecture of the Drosophila testis niche
- PMID: 23364332
- PMCID: PMC3583039
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.089433
Histone demethylase dUTX antagonizes JAK-STAT signaling to maintain proper gene expression and architecture of the Drosophila testis niche
Abstract
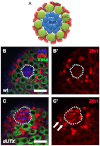
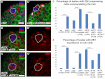
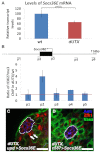
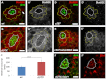
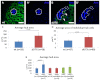
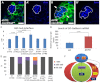
Adult stem cells reside in microenvironments called niches, where they are regulated by both extrinsic cues, such as signaling from neighboring cells, and intrinsic factors, such as chromatin structure. Here we report that in the Drosophila testis niche an H3K27me3-specific histone demethylase encoded by Ubiquitously transcribed tetratricopeptide repeat gene on the X chromosome (dUTX) maintains active transcription of the Suppressor of cytokine signaling at 36E (Socs36E) gene by removing the repressive H3K27me3 modification near its transcription start site. Socs36E encodes an inhibitor of the Janus kinase signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) signaling pathway. Whereas much is known about niche-to-stem cell signaling, such as the JAK-STAT signaling that is crucial for stem cell identity and activity, comparatively little is known about signaling from stem cells to the niche. Our results reveal that stem cells send feedback to niche cells to maintain the proper gene expression and architecture of the niche. We found that dUTX acts in cyst stem cells to maintain gene expression in hub cells through activating Socs36E transcription and preventing hyperactivation of JAK-STAT signaling. dUTX also acts in germline stem cells to maintain hub structure through regulating DE-Cadherin levels. Therefore, our findings provide new insights into how an epigenetic factor regulates crosstalk among different cell types within an endogenous stem cell niche, and shed light on the biological functions of a histone demethylase in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Agger K., Cloos P. A., Christensen J., Pasini D., Rose S., Rappsilber J., Issaeva I., Canaani E., Salcini A. E., Helin K. (2007). UTX and JMJD3 are histone H3K27 demethylases involved in HOX gene regulation and development. Nature 449, 731–734 - PubMed
-
- Bach E. A., Ekas L. A., Ayala-Camargo A., Flaherty M. S., Lee H., Perrimon N., Baeg G. H. (2007). GFP reporters detect the activation of the Drosophila JAK/STAT pathway in vivo. Gene Expr. Patterns 7, 323–331 - PubMed
-
- Becker P. B., Hörz W. (2002). ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 247–273 - PubMed
-
- Beebe K., Lee W. C., Micchelli C. A. (2010). JAK/STAT signaling coordinates stem cell proliferation and multilineage differentiation in the Drosophila intestinal stem cell lineage. Dev. Biol. 338, 28–37 - PubMed
-
- Beuchle D., Struhl G., Müller J. (2001). Polycomb group proteins and heritable silencing of Drosophila Hox genes. Development 128, 993–1004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

