Immune recovery after starting ART in HIV-infected patients presenting and not presenting with tuberculosis in South Africa
- PMID: 23364513
- PMCID: PMC3671097
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318288b39d
Immune recovery after starting ART in HIV-infected patients presenting and not presenting with tuberculosis in South Africa
Abstract
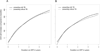
We studied the immune response after starting antiretroviral treatment (ART) in 15,646 HIV-infected patients with or without tuberculosis (TB) at presentation in 3 ART programs in South Africa between 2003 and 2010. Patients presenting with TB had similar increases in CD4 cells compared with all other patients (adjusted difference 4.9 cells/µL per 6 months, 95% confidence interval: 0.2 to 9.7). Younger age, advanced clinical stage, female sex, and lower CD4 cell count at ART start were all associated with steeper CD4 slopes. In South Africa, HIV-infected patients presenting with TB experience immune recovery after starting ART that is no worse than in other patients.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors none to declare
Figures
References
-
- Boulle A, van CG, Hilderbrand K, et al. Seven-year experience of a primary care antiretroviral treatment programme in Khayelitsha, South Africa. AIDS. 2010;24:563–572. - PubMed
-
- Cingolani A, Cozzi LA, Castagna A, et al. Impaired CD4 T-Cell count response to combined antiretroviral therapy in antiretroviral-naive HIV-Infected patients presenting with tuberculosis as AIDS-defining condition. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:853–861. - PubMed
-
- Lawn SD. AIDS in Africa: the impact of coinfections on the pathogenesis of HIV-1 infection. J Infect. 2004;48:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials