Inhibition of p38 MAPK attenuates renal atrophy and fibrosis in a murine renal artery stenosis model
- PMID: 23364805
- PMCID: PMC3625852
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00706.2012
Inhibition of p38 MAPK attenuates renal atrophy and fibrosis in a murine renal artery stenosis model
Abstract
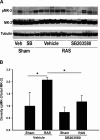
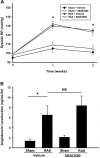
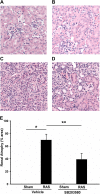
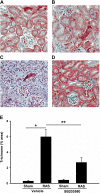
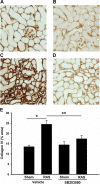
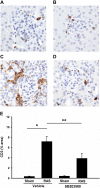
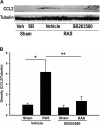
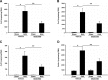
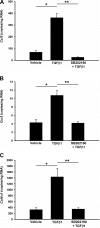
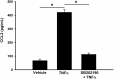
Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is an important cause of chronic renal dysfunction. Recent studies have underscored a critical role for CCL2 (MCP-1)-mediated inflammation in the progression of chronic renal damage in RAS and other chronic renal diseases. In vitro studies have implicated p38 MAPK as a critical intermediate for the production of CCL2. However, a potential role of p38 signaling in the development and progression of chronic renal disease in RAS has not been previously defined. We sought to test the hypothesis that inhibition of p38 MAPK ameliorates chronic renal injury in mice with RAS. We established a murine RAS model by placing a cuff on the right renal artery and treated mice with the p38 inhibitor SB203580 or vehicle for 2 wk. In mice treated with vehicle, the cuffed kidney developed interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, and interstitial inflammation. In mice treated with SB203580, the RAS-induced renal atrophy was reduced (70% vs. 39%, P < 0.05). SB203580 also reduced interstitial inflammation and extracellular matrix deposition but had no effect on the development of hypertension. SB203580 partially blocked the induction of CCL2, CCL7 (MCP-3), CC chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2), and collagen 4 mRNA expression in the cuffed kidneys. In vitro, blockade of p38 hindered both TNF-α and TGF-β-induced CCL2 upregulation. Based on these observations, we conclude that p38 MAPK plays a critical role in the induction of CCL2/CCL7/CCR2 system and the development of interstitial inflammation in RAS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blockade of CCR2 reduces macrophage influx and development of chronic renal damage in murine renovascular hypertension.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Mar 1;310(5):F372-84. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00131.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26661648 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and transforming growth factor-beta1/Smad signaling pathways modulates the development of fibrosis in adriamycin-induced nephropathy.Am J Pathol. 2006 Nov;169(5):1527-40. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060169. Am J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 17071578 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases attenuates renal interstitial fibrosis in a murine unilateral ureteral occlusion model.Life Sci. 2016 Dec 15;167:78-84. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.10.022. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27773718
-
Inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway ameliorates renal fibrosis in an NPHP2 mouse model.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Apr;27(4):1351-8. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr550. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22076433
-
Management of renal artery stenosis: What does the experimental evidence tell us?World J Cardiol. 2014 Aug 26;6(8):855-60. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i8.855. World J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25228964 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of the p38 MAPK pathway attenuates renal injury in pregnant rats with acute necrotizing pancreatitis.Immunol Res. 2021 Jun;69(3):295-306. doi: 10.1007/s12026-021-09195-3. Epub 2021 May 14. Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 33988814
-
Bone morphogenetic protein signaling protects against cerulein-induced pancreatic fibrosis.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 21;9(2):e89114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089114. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586530 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular manifestations of renovascular hypertension in diabetic mice.PeerJ. 2016 Feb 22;4:e1736. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1736. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 26925344 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β1/Smad2/3/Foxp3 signaling is required for chronic stress-induced immune suppression.J Neuroimmunol. 2018 Jan 15;314:30-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 8. J Neuroimmunol. 2018. PMID: 29169800 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CREG1 on Age-Associated Metabolic Phenotypes and Renal Senescence in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 28;22(3):1276. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031276. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33525404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao W, Behm DJ, Nerurkar SS, Ao Z, Bentley R, Mirabile RC, Johns DG, Woods TN, Doe CP, Coatney RW, Ohlstein JF, Douglas SA, Willette RN, Yue TL. Effects of p38 MAPK Inhibitor on angiotensin II-dependent hypertension, organ damage, and superoxide anion production. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 49: 362– 368, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bian ZM, Elner SG, Yoshida A, Kunkel SL, Su J, Elner VM. Activation of p38, ERK1/2 and NIK pathways is required for IL-1β and TNF-α-induced chemokine expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res 73: 111– 121, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Brook M, Tchen CR, Santalucia T, McIlrath J, Arthur JS, Saklatvala J, Clark AR. Posttranslational regulation of tristetraprolin subcellular localization and protein stability by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. Mol Cell Biol 26: 2408– 2418, 2006 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng J, Diaz Encarnacion MM, Warner GM, Gray CE, Nath KA, Grande JP. TGF-β1 stimulates monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in mesangial cells through a phosphodiesterase isoenzyme 4-dependent process. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 289: C959– C970, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

