Hemodynamic instability during carotid angioplasty and stenting-relationship of calcified plaque and its characteristics
- PMID: 23364959
- PMCID: PMC3575967
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.295
Hemodynamic instability during carotid angioplasty and stenting-relationship of calcified plaque and its characteristics
Abstract
Purpose: During carotid angioplasty and stenting (CAS), hemodynamic instability (HDI) can occur, possibly causing post-procedural ischemic complications. The goal of this study was to investigate the risk factors of HDI focusing on characteristics of plaque.
Materials and methods: Thirty nine CAS patients were retrospectively evaluated for HDI. Prolonged HDI that lasted over 30 minutes was analyzed in relation to characteristics of calcified plaque.
Results: Nineteen (48.7%) patients had HDI. Ten of the 19 had both bradycardia and hypotension, and nine had only bradycardia. All bradycardia was treated well with a transcutaneous temporary cardiac pacemaker. But eight patients presented with prolonged hypotension in spite of recovery of bradycardia. Calcified plaque was a related factor associated with HDI (odds ratio, 8.571; 95% confidence interval, 1.321-55.62; p=0.024). Extensive and eccentric type calcified plaques were associated with prolonged hypotension (p=0.04, and p=0.028, respectively).
Conclusion: The calcification of plaque is a predictable factor of HDI during CAS, and its extensive and eccentric calcified plaques may be related to prolonged HDI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
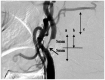
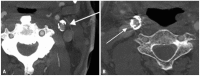
Similar articles
-
Prediction of Prolonged Hemodynamic Instability During Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting.Neurointervention. 2016 Sep;11(2):120-6. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2016.11.2.120. Epub 2016 Sep 3. Neurointervention. 2016. PMID: 27621949 Free PMC article.
-
Periprocedural hemodynamic instability with carotid angioplasty and stenting.Surg Neurol. 2008 Sep;70(3):279-85; discussion 285-6. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2007.07.006. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Surg Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18262636
-
Relationship between annular calcification of plaques in the carotid sinus and perioperative hemodynamic disorder in carotid angioplasty and stenting.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022 Oct;31(10):106634. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2022.106634. Epub 2022 Aug 10. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022. PMID: 35963212
-
Hemodynamic instability after extracranial carotid stenting.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006 Jun;148(6):639-45. doi: 10.1007/s00701-006-0752-2. Epub 2006 Mar 8. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006. PMID: 16523226
-
Factors associated with hemodynamic instability following carotid artery stenting.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021 Apr;203:106589. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2021.106589. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 33706060
Cited by
-
The Prevalence and Factors Contributing to Hemodynamic Depression in Patients Undergoing Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting.J Vasc Interv Neurol. 2015 Oct;8(4):5-10. J Vasc Interv Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26600923 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Prolonged Hemodynamic Instability During Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting.Neurointervention. 2016 Sep;11(2):120-6. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2016.11.2.120. Epub 2016 Sep 3. Neurointervention. 2016. PMID: 27621949 Free PMC article.
-
Complications and Predictors of Hypotension Requiring Vasopressor after Carotid Artery Stenting.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2017 Mar 15;57(3):115-121. doi: 10.2176/nmc.oa.2016-0155. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2017. PMID: 28154342 Free PMC article.
-
Recurrent dizziness due to paroxysmal atrioventricular block following carotid artery stenting in a patient with a normal atrioventricular conduction and iatrogenic carotid sinus syndrome.HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2024 Jun 19;10(9):630-634. doi: 10.1016/j.hrcr.2024.06.007. eCollection 2024 Sep. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39355825 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Carotid interventions and blood pressure.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2014 Dec;164(23-24):503-7. doi: 10.1007/s10354-014-0327-4. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2014. PMID: 25394988
References
-
- Dietz A, Berkefeld J, Theron JG, Schmitz-Rixen T, Zanella FE, Turowski B, et al. Endovascular treatment of symptomatic carotid stenosis using stent placement: long-term follow-up of patients with a balanced surgical risk/benefit ratio. Stroke. 2001;32:1855–1859. - PubMed
-
- Brown MM, Venables G, Clifton A, Gaines P, Taylor RS. Carotid endarterectomy vs carotid angioplasty. Lancet. 1997;349:880–881. - PubMed
-
- Brooks WH, McClure RR, Jones MR, Coleman TL, Breathitt L. Carotid angioplasty and stenting versus carotid endarterectomy for treatment of asymptomatic carotid stenosis: a randomized trial in a community hospital. Neurosurgery. 2004;54:318–324. - PubMed
-
- Schulz UG, Rothwell PM. Sex differences in carotid bifurcation anatomy and the distribution of atherosclerotic plaque. Stroke. 2001;32:1525–1531. - PubMed
-
- Cayne NS, Faries PL, Trocciola SM, Saltzberg SS, Dayal RD, Clair D, et al. Carotid angioplasty and stent-induced bradycardia and hypotension: impact of prophylactic atropine administration and prior carotid endarterectomy. J Vasc Surg. 2005;41:956–961. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

