Anti-allodynic effects of levodopa in neuropathic rats
- PMID: 23364964
- PMCID: PMC3575974
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.330
Anti-allodynic effects of levodopa in neuropathic rats
Abstract
Purpose: Levodopa is the most effective anti-Parkinsonian agent. It has also been known to exhibit analgesic properties in laboratory and clinical settings. However, studies evaluating its effects on neuropathic pain are limited. The aim of the present study was to examine the anti-allodynic effects of levodopa in neuropathic rats.
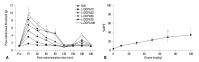
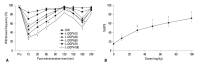
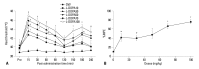
Materials and methods: Sprague-Dawley male rats underwent the surgical procedure for L5 and L6 spinal nerves ligation. Sixty neuropathic rats were randomly divided into 6 groups for the oral administration of distilled water and levodopa at 10, 30, 50, 70, and 100 mg/kg, respectively. We co-administered carbidopa with levodopa to prevent peripheral synthesis of dopamine from levodopa, and observed tactile, cold, and heat allodynia pre-administration, and at 15, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, and 240 min after drug administration. We also measured locomotor function of neuropathic rats using rotarod test to examine whether levodopa caused side effects or not.
Results: Distilled water group didn't show any difference in all allodynia. For the levodopa groups (10-100 mg/kg), tactile and heat withdrawal thresholds were increased, and cold withdrawal frequency was decreased dose-dependently (p<0.01). In addition, levodopa induced biphasic analgesia. Different dosage of levodopa did not impact on the rotarod time (p>0.05).
Conclusion: Levodopa reversed tactile, cold and heat allodynia in neuropathic rat without any side effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Levodopa analgesia in experimental neuropathic pain.Brain Res Bull. 2010 Nov 20;83(6):304-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2010.08.012. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Brain Res Bull. 2010. PMID: 20813171
-
The antinociceptive effect of acetaminophen in a rat model of neuropathic pain.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2012 May;28(5):251-8. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2011.11.003. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22531303 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 on mechanical and cold allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain.Anesth Analg. 2009 Jun;108(6):1958-63. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31819f1972. Anesth Analg. 2009. PMID: 19448231
-
A hydro-ethanolic extract of Synedrella nodiflora (L.) Gaertn ameliorates hyperalgesia and allodynia in vincristine-induced neuropathic pain in rats.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;26(4):383-94. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2014-0084. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25720058
-
[Clinical studies with levodopa/carbidopa intestinal gel].Ideggyogy Sz. 2014 Jan 30;67(1-2):5-8. Ideggyogy Sz. 2014. PMID: 24654442 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Dorsal root ganglion neurons and tyrosine hydroxylase--an intriguing association with implications for sensation and pain.Pain. 2016 Feb;157(2):314-320. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000381. Pain. 2016. PMID: 26447702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pramipexole treatment attenuates mechanical hypersensitivity in male rats experiencing chronic inflammatory pain.Neuropharmacology. 2022 May 1;208:108976. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.108976. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Neuropharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35085583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mercuri NB, Bernardi G. The 'magic' of L-dopa: why is it the gold standard Parkinson's disease therapy? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005;26:341–344. - PubMed
-
- Conti CF, de Oliveira MM, Andriolo RB, Saconato H, Atallah AN, Valbuza JS, et al. Levodopa for idiopathic restless legs syndrome: evidence-based review. Mov Disord. 2007;22:1943–1951. - PubMed
-
- Nixon DW. Letter: use of L-dopa to relieve pain from bone metastases. N Engl J Med. 1975;292:647. - PubMed
-
- Ertas M, Sagduyu A, Arac N, Uludag B, Ertekin C. Use of levodopa to relieve pain from painful symmetrical diabetic polyneuropathy. Pain. 1998;75:257–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

