Interleukin-10 down-regulates cathepsin B expression in fetal rat alveolar type II cells exposed to hyperoxia
- PMID: 23364980
- PMCID: PMC3575969
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.445
Interleukin-10 down-regulates cathepsin B expression in fetal rat alveolar type II cells exposed to hyperoxia
Abstract
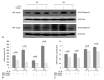
Purpose: Hyperoxia has the chief biological effect of cell death. We have previously reported that cathepsin B (CB) is related to fetal alveolar type II cell (FATIIC) death and pretreatment of recombinant IL-10 (rIL-10) attenuates type II cell death during 65%-hyperoixa. In this study, we investigated what kinds of changes of CB expression are induced in FATIICs at different concentrations of hyperoxia (65%- and 85%-hyperoxia) and whether pretreatment with rIL-10 reduces the expression of CB in FATIICs during hyperoxia.
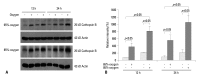
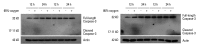
Materials and methods: Isolated embryonic day 19 fetal rat alveolar type II cells were cultured and exposed to 65%- and 85%-hyperoxia for 12 h and 24 h. Cells in room air were used as controls. Cytotoxicity was assessed by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) released into the supernatant. Expression of CB was analyzed by fluorescence-based assay upon cell lysis and western blotting, and LDH-release was re-analyzed after preincubation of cathepsin B-inhibitor (CBI). IL-10 production was analyzed by ELISA, and LDH-release was re-assessed after preincubation with rIL-10 and CB expression was re-analyzed by western blotting and real-time PCR.
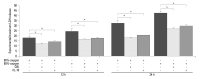
Results: LDH-release and CB expression in FATIICs were enhanced significantly in an oxygen-concentration-dependent manner during hyperoxia, whereas caspase-3 was not activated. Preincubation of FATIICs with CBI significantly reduced LDH-release during hyperoxia. IL-10-release decreased in an oxygen-concentration-dependent fashion, and preincubation of the cells with rIL-10 significantly reduced cellular necrosis and expression of CB in FATIICs which were exposed to 65%- and 85%-hyperoxia.
Conclusion: Our study suggests that CB is enhanced in an oxygen- concentration-dependent manner, and IL-10 has an inhibitory effect on CB expression in FATIICs during hyperoxia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
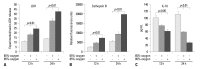
Similar articles
-
rIL-10 enhances IL-10 signalling proteins in foetal alveolar type II cells exposed to hyperoxia.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Jul;19(7):1538-47. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12596. Epub 2015 Jun 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26059905 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin B is activated as an executive protease in fetal rat alveolar type II cells exposed to hyperoxia.Exp Mol Med. 2011 Apr 30;43(4):223-9. doi: 10.3858/emm.2011.43.4.027. Exp Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21415591 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of recombinant IL-10 on cultured fetal rat alveolar type II cells exposed to 65%-hyperoxia.Respir Res. 2011 May 24;12(1):68. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-12-68. Respir Res. 2011. PMID: 21609457 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-24 as a Pulmonary Target Cytokine in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021 Jun;79(2):311-320. doi: 10.1007/s12013-021-00968-z. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 33683657
-
[Protective effects of amygdalin on hyperoxia-exposed type II alveolar epithelial cells isolated from premature rat lungs in vitro].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2005 Feb;43(2):118-23. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15833168 Chinese.
Cited by
-
IL-10 restricts dendritic cell (DC) growth at the monocyte-to-monocyte-derived DC interface by disrupting anti-apoptotic and cytoprotective autophagic molecular machinery.Immunol Res. 2015 Dec;63(1-3):131-43. doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8700-y. Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26395023
-
rIL-10 enhances IL-10 signalling proteins in foetal alveolar type II cells exposed to hyperoxia.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 Jul;19(7):1538-47. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12596. Epub 2015 Jun 8. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26059905 Free PMC article.
-
NLRX1 knockdown attenuates pro-apoptotic signaling and cell death in pulmonary hyperoxic acute injury.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 1;13(1):3441. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28206-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36859435 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of recombinant interleukin-10 on newborn rat lungs exposed to short-term sublethal hyperoxia.Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024 Oct;67(10):540-549. doi: 10.3345/cep.2024.01221. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39327683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee PJ, Choi AM. Pathways of cell signaling in hyperoxia. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003;35:341–350. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Yuan X, Nordgren G, Dalen H, Dubowchik GM, Firestone RA, et al. Induction of cell death by the lysosomotropic detergent MSDH. FEBS Lett. 2000;470:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Bröker LE, Huisman C, Span SW, Rodriguez JA, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G. Cathepsin B mediates caspase-independent cell death induced by microtubule stabilizing agents in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:27–30. - PubMed
-
- Layton GT, Harris SJ, Bland FA, Lee SR, Fearn S, Kaleta J, et al. Therapeutic effects of cysteine protease inhibition in allergic lung inflammation: inhibition of allergen-specific T lymphocyte migration. Inflamm Res. 2001;50:400–408. - PubMed
-
- Tang PS, Tsang ME, Lodyga M, Bai XH, Miller A, Han B, et al. Lipopolysaccharide accelerates caspase-independent but cathepsin B-dependent death of human lung epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209:457–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

