Top-down modulation of lateral interactions in visual cortex
- PMID: 23365217
- PMCID: PMC3711382
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3825-12.2013
Top-down modulation of lateral interactions in visual cortex
Abstract
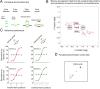
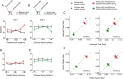
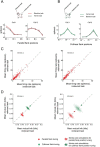
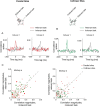
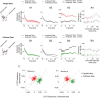
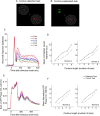
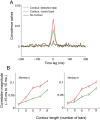
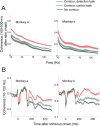
The primary visual cortex (V1) changes its computation according to the perceptual task being performed. We propose that this cognitive modulation results from gating of V1 intrinsic connections. To test this idea, using behavioral paradigms that engage top-down modulation of V1 contextual interactions, we recorded from chronically implanted electrode arrays in macaques. We observed task-dependent changes in interactions between V1 sites measured both by correlation between spike trains and by coherence between local field potentials (LFP-LFP coherence). The direction of the changes in aggregate activity, as measured by LFPs, depended on perceptual strategy: perceptual grouping increased LFP coherence between sites crucial for the task, whereas perceptual segregation lowered the LFP coherence. Using spiking activity as a measure, we found that the behaviorally driven changes in correlation structure between neurons dramatically increased the stimulus-related information that they convey; this additional increase in encoded information at the level of neuronal ensembles equals that obtained from task-driven reconfigurations of neural tuning curves. The improvements in information encoding were strongest for stimuli with greatest discrimination difficulty.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of the primary visual cortex in perceptual suppression of salient visual stimuli.J Neurosci. 2010 Sep 15;30(37):12353-65. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0677-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20844131 Free PMC article.
-
Attention reduces stimulus-driven gamma frequency oscillations and spike field coherence in V1.Neuron. 2010 Apr 15;66(1):114-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.03.013. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 20399733 Free PMC article.
-
Robust gamma coherence between macaque V1 and V2 by dynamic frequency matching.Neuron. 2013 May 8;78(3):523-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.03.003. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23664617
-
The maximum range and timing of excitatory contextual modulation in monkey primary visual cortex.Vis Neurosci. 2006 Sep-Oct;23(5):721-8. doi: 10.1017/S0952523806230049. Vis Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17020628 Review.
-
Regulation of spike timing in visual cortical circuits.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008 Feb;9(2):97-107. doi: 10.1038/nrn2315. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18200026 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond Rehabilitation of Acuity, Ocular Alignment, and Binocularity in Infantile Strabismus.Front Syst Neurosci. 2018 Jul 18;12:29. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2018.00029. eCollection 2018. Front Syst Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30072876 Free PMC article.
-
Linking structure and function: development of lateral spatial interactions in macaque monkeys.Vis Neurosci. 2013 Nov;30(5-6):263-70. doi: 10.1017/S0952523813000394. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Vis Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24107405 Free PMC article.
-
Profile of Charles D. Gilbert.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Oct 3;114(40):10517-10519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1714690114. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28973858 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Binocular flash suppression in the primary visual cortex of anesthetized and awake macaques.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 12;9(9):e107628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107628. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25216188 Free PMC article.
-
Uniting functional network topology and oscillations in the fronto-parietal single unit network of behaving primates.Elife. 2016 Aug 15;5:e15719. doi: 10.7554/eLife.15719. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27525488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott LF, Dayan P. The effect of correlated variability on the accuracy of a population code. Neural Comput. 1999;11:91–101. - PubMed
-
- Aertsen AM, Gerstein GL, Habib MK, Palm G. Dynamics of neuronal firing correlation: modulation of “effective connectivity.”. J Neurophysiol. 1989;61:900–917. - PubMed
-
- Allman J, Miezin F, McGuinness E. Stimulus specific responses from beyond the classical receptive field: neurophysiological mechanisms for local-global comparisons in visual neurons. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1985;8:407–430. - PubMed
-
- Averbeck BB, Latham PE, Pouget A. Neural correlations, population coding and computation. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:358–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
