Adaptation improves neural coding efficiency despite increasing correlations in variability
- PMID: 23365247
- PMCID: PMC6619115
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3449-12.2013
Adaptation improves neural coding efficiency despite increasing correlations in variability
Abstract
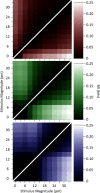
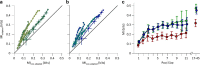
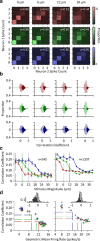
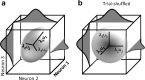
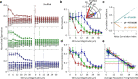
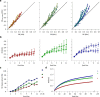
Exposure of cortical cells to sustained sensory stimuli results in changes in the neuronal response function. This phenomenon, known as adaptation, is a common feature across sensory modalities. Here, we quantified the functional effect of adaptation on the ensemble activity of cortical neurons in the rat whisker-barrel system. A multishank array of electrodes was used to allow simultaneous sampling of neuronal activity. We characterized the response of neurons to sinusoidal whisker vibrations of varying amplitude in three states of adaptation. The adaptors produced a systematic rightward shift in the neuronal response function. Consistently, mutual information revealed that peak discrimination performance was not aligned to the adaptor but to test amplitudes 3-9 μm higher. Stimulus presentation reduced single neuron trial-to-trial response variability (captured by Fano factor) and correlations in the population response variability (noise correlation). We found that these two types of variability were inversely proportional to the average firing rate regardless of the adaptation state. Adaptation transferred the neuronal operating regime to lower rates with higher Fano factor and noise correlations. Noise correlations were positive and in the direction of signal, and thus detrimental to coding efficiency. Interestingly, across all population sizes, the net effect of adaptation was to increase the total information despite increasing the noise correlation between neurons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stimulus-specific and stimulus-nonspecific firing synchrony and its modulation by sensory adaptation in the whisker-to-barrel pathway.J Neurophysiol. 2009 May;101(5):2328-38. doi: 10.1152/jn.91151.2008. Epub 2009 Mar 11. J Neurophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19279146 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation in the neural code for whisker deflection direction along the lemniscal pathway.J Neurophysiol. 2009 Nov;102(5):2771-80. doi: 10.1152/jn.00636.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 9. J Neurophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19741100 Free PMC article.
-
Encoding of whisker vibration by rat barrel cortex neurons: implications for texture discrimination.J Neurosci. 2003 Oct 8;23(27):9146-54. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-27-09146.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14534248 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal adaptation in the somatosensory system of rodents.Neuroscience. 2017 Feb 20;343:66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.11.043. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 27923742 Review.
-
Neural coding: A single neuron's perspective.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018 Nov;94:238-247. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018. PMID: 30227142 Review.
Cited by
-
Adaptive shaping of cortical response selectivity in the vibrissa pathway.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Jun 1;113(10):3850-65. doi: 10.1152/jn.00978.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 18. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25787959 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulus-Specific Adaptation Decreases the Coupling of Spikes to LFP Phase.Front Neural Circuits. 2019 Jul 3;13:44. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2019.00044. eCollection 2019. Front Neural Circuits. 2019. PMID: 31333419 Free PMC article.
-
Population decoding in rat barrel cortex: optimizing the linear readout of correlated population responses.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Jan;10(1):e1003415. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003415. Epub 2014 Jan 2. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 24391487 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of Population Activity in Rat Sensory Cortex: Network Correlations Predict Anatomical Arrangement and Information Content.Front Neural Circuits. 2016 Jul 6;10:49. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2016.00049. eCollection 2016. Front Neural Circuits. 2016. PMID: 27458347 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and long-lasting improvements in neural discrimination of acoustic signals with passive familiarization.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 29;14(8):e0221819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221819. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31465431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott LF, Dayan P. The effect of correlated variability on the accuracy of a population code. Neural Comput. 1999;11:91–101. - PubMed
-
- Abbott LF, Rajan K, Sompolinsky H. Interactions between intrinsic and stimulus-evoked activity in recurrent neural networks. In: Ding M, Glanzman DL, editors. The Dynamic brain: an exploration of neuronal variability and its functional significance. New York: Oxford UP; 2011. pp. 65–82.
-
- Adibi M, Arabzadeh E. A comparison of neuronal and behavioral detection and discrimination performances in rat whisker system. J Neurophysiol. 2011;105:356–365. - PubMed
-
- Ahissar E, Knutsen PM. Object localization with whiskers. Biological Cybernetics. 2008;98:449–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
