Does the panoramic radiography have the power to identify the gonial angle in orthodontics?
- PMID: 23365514
- PMCID: PMC3532868
- DOI: 10.1100/2012/219708
Does the panoramic radiography have the power to identify the gonial angle in orthodontics?
Abstract
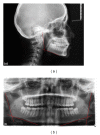
Purpose: The objective of this study was to assess gonial angle under the angle classification by comparing panoramic radiograph and lateral cephalometric radiograph.
Materials and methods: 49 patients (25 males, 24 females) with an age range of 12-29 years participated in the present study. Subjects were retrospectively selected among those categorised as skeletal and dental Class I, II, and III malocclusion group. Using lateral cephalometric radiograph, mandibular and ramal planes were drawn and based on these planes. Gonial angle was determined from two tangents which were drawn from the inferior border of the mandible and posterior borders of the condyle and ramus of both sides in the panoramic radiographs. Multiple comparison tests (ANOVA) were used to determine differences between the three angle groups.
Results: There were no significant differences between Class I, II, and III malocclusion group values of gonial angles determined by lateral cephalometric radiograph and panoramic radiographs (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Panoramic radiograph results were shown to be as reliable as lateral cephalometric radiograph in all angle classifications. Panoramic radiography can be used as an alternative radiographic technique to detect gonial angle in orthodontic patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dilemma of gonial angle measurement: Panoramic radiograph or lateral cephalogram.Imaging Sci Dent. 2017 Jun;47(2):93-97. doi: 10.5624/isd.2017.47.2.93. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Imaging Sci Dent. 2017. PMID: 28680845 Free PMC article.
-
Panoramic radiographs: determination of mandibular steepness.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2005 Winter;29(2):165-6. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2005. PMID: 15719923
-
Björk-Jarabak cephalometric analysis on CBCT synthesized cephalograms with different dentofacial sagittal skeletal patterns.Dental Press J Orthod. 2014 Nov-Dec;19(6):46-53. doi: 10.1590/2176-9451.19.6.046-053.oar. Dental Press J Orthod. 2014. PMID: 25628079 Free PMC article.
-
[Research methods in dentistry 9. Follow-up of permucosal implants in an edentate mandible using panoramic radiography].Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2005 Mar;112(3):86-9. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2005. PMID: 15792391 Review. Dutch.
-
Orthodontic radiology: a review.Int Dent J. 1987 Mar;37(1):16-24. Int Dent J. 1987. PMID: 3294596 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Gonial Angle With Age and Gender Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Images.Cureus. 2022 May 14;14(5):e24997. doi: 10.7759/cureus.24997. eCollection 2022 May. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35719831 Free PMC article.
-
Age and gender correlation of gonial angle, ramus height and bigonial width in dentate subjects in a dental school in Far North Queensland.J Clin Exp Dent. 2016 Feb 1;8(1):e49-54. doi: 10.4317/jced.52683. eCollection 2016 Feb. J Clin Exp Dent. 2016. PMID: 26855706 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the validity of orthopantomographs in the evaluation of mandibular steepness in Libya.J Orthod Sci. 2018 Jun 6;7:14. doi: 10.4103/jos.JOS_148_17. eCollection 2018. J Orthod Sci. 2018. PMID: 29963509 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of edentulism on mandibular morphology: evaluation of panoramic radiographs.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:254932. doi: 10.1155/2014/254932. Epub 2014 Aug 18. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 25202718 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Analysis of the Correlation Between Mandibular Gonial Angle and Incidence of Mandibular Angle Fracture-A Radiomorphometric Study.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2025 Apr;24(2):372-380. doi: 10.1007/s12663-024-02300-7. Epub 2024 Aug 12. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2025. PMID: 40182469
References
-
- Yanikoğlu N, Yilmaz B. Radiological evaluation of changes in the gonial angle after teeth extraction and wearing of dentures: a 3-year longitudinal study. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontology. 2008;105(6):e55–e60. - PubMed
-
- Kasai K, Richards LC, Kanazawa E, Ozaki T, Iwasawa T. Relationship between attachment of the superficial masseter muscle and craniofacial morphology in dentate and edentulous humans. Journal of Dental Research. 1994;73(6):1142–1149. - PubMed
-
- Xiao D, Gao H, Ren Y. Craniofacial morphological characteristics of Chinese adults with normal occlusion and different skeletal divergence. European Journal of Orthodontics. 2011;33(2):198–204. - PubMed
-
- Nanda SK. Growth patterns in subjects with long and short faces. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. 1990;98(3):247–258. - PubMed
-
- Tahmina K, Tanaka E, Tanne K. Craniofacial morphology in orthodontically treated patients of class III malocclusion with stable and unstable treatment outcomes. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. 2000;117(6):681–690. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical