Modeling Airflow Using Subject-Specific 4DCT-Based Deformable Volumetric Lung Models
- PMID: 23365554
- PMCID: PMC3539421
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/350853
Modeling Airflow Using Subject-Specific 4DCT-Based Deformable Volumetric Lung Models
Abstract
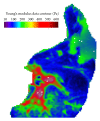
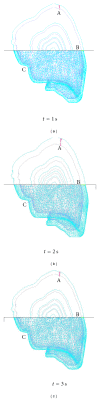
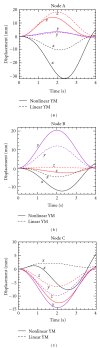
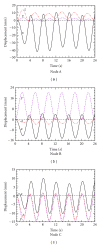
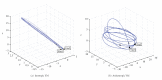
Lung radiotherapy is greatly benefitted when the tumor motion caused by breathing can be modeled. The aim of this paper is to present the importance of using anisotropic and subject-specific tissue elasticity for simulating the airflow inside the lungs. A computational-fluid-dynamics (CFD) based approach is presented to simulate airflow inside a subject-specific deformable lung for modeling lung tumor motion and the motion of the surrounding tissues during radiotherapy. A flow-structure interaction technique is employed that simultaneously models airflow and lung deformation. The lung is modeled as a poroelastic medium with subject-specific anisotropic poroelastic properties on a geometry, which was reconstructed from four-dimensional computed tomography (4DCT) scan datasets of humans with lung cancer. The results include the 3D anisotropic lung deformation for known airflow pattern inside the lungs. The effects of anisotropy are also presented on both the spatiotemporal volumetric lung displacement and the regional lung hysteresis.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Computational fluid dynamics modeling of airflow inside lungs using heterogenous anisotropic lung tissue elastic properties.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2012;173:205-11. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2012. PMID: 22356987
-
Analytic Intermodel Consistent Modeling of Volumetric Human Lung Dynamics.J Biomech Eng. 2015 Oct;137(10):101005. doi: 10.1115/1.4031349. J Biomech Eng. 2015. PMID: 26292034
-
A 4DCT imaging-based breathing lung model with relative hysteresis.J Comput Phys. 2016 Dec 1;326:76-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2016.08.039. Epub 2016 Aug 31. J Comput Phys. 2016. PMID: 28260811 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of 3D volumetric lung dynamics for real-time external beam lung radiotherapy.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2011;163:567-73. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2011. PMID: 21335858
-
Computational fluid dynamics modelling of human upper airway: A review.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Nov;196:105627. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105627. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32629222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Surface deformation analysis of collapsed lungs using model-based shape matching.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019 Oct;14(10):1763-1774. doi: 10.1007/s11548-019-02013-0. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2019. PMID: 31250255 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid, image-based and biomechanics-based registration approach to markerless intraoperative nodule localization during video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery.Med Image Anal. 2021 Apr;69:101983. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.101983. Epub 2021 Jan 30. Med Image Anal. 2021. PMID: 33588119 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling and incorporating cardiac-induced lung tissue motion in a breathing motion model.Med Phys. 2014 Apr;41(4):043501. doi: 10.1118/1.4866888. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24694158 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keall PJ, Mageras GS, Balter JM, et al. The management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology report of AAPM Task Group 76. Medical Physics. 2006;33(10):3874–3900. - PubMed
-
- Santhanam AP, Willoughby T, Shah A, Meeks S, Rolland JP, Kupelian P. Real-time simulation of 4D lung tumor radiotherapy using a breathing model. Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention; 2008; pp. 710–771. - PubMed
-
- Guckenberger M, Richter A, Boda-Heggermann J, Lohr F. Motion compensation in radiotherapy. Critical Reviews in Biomedical Engineering . 2012;40(3):187–197. - PubMed
-
- Anderson J. Computational Fluid Dynamics—The Basics with Applications. Mcgraw-Hill Science;
-
- Santhanam AP, Hamza-Lup FG, Rolland JP. Simulating 3-D lung dynamics using a programmable graphics processing unit. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine. 2007;11(5):497–506. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

