The risk of acute kidney injury and its impact on 30-day and long-term mortality after transcatheter aortic valve implantation
- PMID: 23365748
- PMCID: PMC3541560
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/483748
The risk of acute kidney injury and its impact on 30-day and long-term mortality after transcatheter aortic valve implantation
Abstract
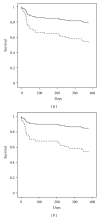
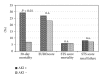
Background. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) is widely used in high risk patients (pts) with aortic stenosis. Underlying chronic kidney disease implicates a high risk of postprocedural acute kidney injury (AKI). We analyzed its occurrence, impact on hospital stay, and mortality. Methods. 150 consecutive pts underwent TAVI in our institution (mean age 81 ± 7 years; logistic EuroSCORE 24 ± 15%). AKI definition was a creatinine rise of 26.5 μmol/L or more within 48 hours postprocedural. Ten patients on chronic hemodialysis were excluded. Results. AKI occurred in 28 pts (20%). Baseline creatinine was higher in AKI pts (126.4 ± 59.2 μmol/L versus 108.7 ± 45.1 μmol/L, P = 0.09). Contrast media use was distributed evenly. Both, 30-day mortality (29% versus 7%, P < 0.0001) and long-term mortality (43% versus 18%, P < 0.0001) were higher; hospital stay was longer in AKI pts (20 ± 12 versus 15 ± 10 days, P = 0.03). Predicted renal failure calculated STS Score was similar (8.0 ± 5.0% [AKI] versus 7.1 ± 4.0% [non-AKI], P = 0.32) and estimated lower renal failure rates than observed. Conclusion. AKI remains a frequent complication with increased mortality in TAVI pts. Careful identification of risk factors and development of more suitable risk scores are essential.
Figures
References
-
- Iung B, Baron G, Butchart EG, et al. A prospective survey of patients with valvular heart disease in Europe: the Euro Heart Survey on valvular heart disease. European Heart Journal . 2003;24(13):1231–1243. - PubMed
-
- Sack S, Schofer J. Transcatheter-based aortic valve implantation. Present and future technologies. Herz . 2009;34(5):357–366. - PubMed
-
- Cribier A, Eltchaninoff H, Bash A, et al. Percutaneous transcatheter implantation of an aortic valve prosthesis for calcific aortic stenosis: first human case description. Circulation . 2002;106(24):3006–3008. - PubMed
-
- McCullough PA. Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Journal of the American College of Cardiology . 2008;51(15):1419–1428. - PubMed
-
- Lindsay J, Apple S, Pinnow EE, et al. Percutaneous coronary intervention-associated nephropathy foreshadows increased risk of late adverse events in patients with normal baseline serum creatinine. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions . 2003;59(3):338–343. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

