Swept source optical coherence tomography based smart handheld vitreoretinal microsurgical tool for tremor suppression
- PMID: 23366163
- PMCID: PMC3672223
- DOI: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346202
Swept source optical coherence tomography based smart handheld vitreoretinal microsurgical tool for tremor suppression
Abstract
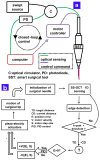
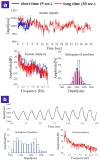
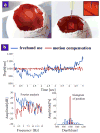
Microsurgeons require the ability to make precise and stable maneuvers in order to achieve surgical objectives and to minimize surgical risks during freehand microsurgical procedures. This work presents a novel common path swept source optical coherence tomography based smart surgical tool that suppresses hand tremor. It allows enhanced tool tip stabilization, more accurate targeting and may lower surgical risk. Here the one dimensional motion tremor of a surgeon's hand is assessed by the surgical instrument. The ability to accurately locate a surgical target and the ability to maintain tool tip offset distances in a chicken embryo model are significantly improved as compared to freehand use.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Active tremor cancellation by a "smart" handheld vitreoretinal microsurgical tool using swept source optical coherence tomography.Opt Express. 2012 Oct 8;20(21):23414-21. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.023414. Opt Express. 2012. PMID: 23188305 Free PMC article.
-
Force sensing micro-forceps for robot assisted retinal surgery.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012;2012:1401-4. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346201. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012. PMID: 23366162 Free PMC article.
-
Ball Lens Fiber Optic Sensor based Smart Handheld Microsurgical Instrument.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2013 Mar 20;8576:10.1117/12.2004947. doi: 10.1117/12.2004947. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2013. PMID: 24224076 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted tremor control for performance enhancement of retinal microsurgeons.Br J Ophthalmol. 2019 Aug;103(8):1195-1200. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-313318. Epub 2018 Dec 20. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30573495 Review.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography for Retinal Surgery: Perioperative Analysis to Real-Time Four-Dimensional Image-Guided Surgery.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016 Jul 1;57(9):OCT37-50. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-19277. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 27409495 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overcoming the impact of physiologic tremors in ophthalmology.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022 Dec;260(12):3723-3736. doi: 10.1007/s00417-022-05718-2. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35788893 Free PMC article.
-
Unintentional Movements During the Use of Vitreoretinal Forceps.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2018 Dec 21;7(6):28. doi: 10.1167/tvst.7.6.28. eCollection 2018 Nov. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2018. PMID: 30619648 Free PMC article.
-
Development and preliminary results of bimanual smart micro-surgical system using a ball-lens coupled OCT distance sensor.Biomed Opt Express. 2016 Oct 31;7(11):4816-4826. doi: 10.1364/BOE.7.004816. eCollection 2016 Nov 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2016. PMID: 27896018 Free PMC article.
-
The Surgeon's Role in Inducing and Controlling Motion Errors During Intraocular Membrane Peeling Procedures.Turk J Ophthalmol. 2021 Oct 26;51(5):288-293. doi: 10.4274/tjo.galenos.2020.40035. Turk J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34702022 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted vitreoretinal surgery: current perspectives.Robot Surg. 2018;5:1-11. doi: 10.2147/RSRR.S122301. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Robot Surg. 2018. PMID: 29527537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riviere C, Gangloff J, Mathelin M. Robotic Compensation of Biological Motion to Enhance Surgical Accuracy. Proc Of the IEEE. 2006;94(9):1705–1716.
-
- Horio N, Horiguchi M, Yamamoto N. Triamcinolone-Assisted Internal Limiting Membrane Peeling During Idiopathic Macular Hole Surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123:96–99. - PubMed
-
- Murthy RK, Chalam KV. Assistant-Independent OptiFlex System for Contact and Noncontact Wide-Angle Viewing in Vitreoretinal Surgery. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010;128:490–492. - PubMed
-
- Taylor R, Jensen P, Whitcomb L, Barnes A, Kumar R, Stoianovici D, Gupta P, Wang Z, de Juan E, Jr, Kavoussi L. A steady-hand robotic system for microsurgical augmentation. Int J Robot Res. 1999;18:1201–1210.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
