Handheld micromanipulator for robot-assisted stapes footplate surgery
- PMID: 23366167
- PMCID: PMC3561930
- DOI: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346206
Handheld micromanipulator for robot-assisted stapes footplate surgery
Abstract
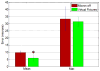
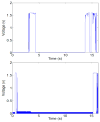
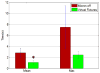
Stapes footplate surgery is complex and delicate. This surgery is carried out in the middle ear to improve hearing. High accuracy is required to avoid critical tissues and structures near the surgical worksite. By suppressing the surgeon's tremor during the operation, accuracy can be improved. In this paper, a fully handheld active micromanipulator known as Micron is evaluated for its feasibility for this delicate operation. An ergonomic handle, a custom tip, and a brace attachment were designed for stapes footplate surgery and tested in a fenestration task through a fixed speculum. Accuracy was measured during simulated surgery in two different scenarios: Micron off (unaided) and Micron on (aided), both with image guidance. Preliminary results show that Micron significantly reduces the mean position error and the mean duration of time spent in specified dangerous zones.
Figures





References
-
- Shea JJ., Jr Forty years of stapes surgery. Am J Otol. 1998;19:52–55. - PubMed
-
- Sedwick JD, Louden CL, Shelton C. Stapedectomy vs stapedotomy: Do you really need a laser? Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997;123(2):177–180. - PubMed
-
- Rothbaum DL, Roy J, Stoianovici D, Berkelman P, Hager GD, Taylor RH, Whitcomb LL, Francis HW, Niparko JK. Robot-assisted stapedotomy: micropick fenestration of the stapes footplate. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002;127:417–426. - PubMed
-
- Kazmitcheff G, Miroir M, Nguyen Y, Celerier C, Mazalaigue S, Ferrary E, Sterkers O, Grayeli AB. Evaluation of command modes of an assistance robot for middle ear surgery. Proc IEEE Intl Conf Intell Robot Syst. 2011:2532–2538.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
