Audio-visual feedback for electromyographic control of vowel synthesis
- PMID: 23366706
- PMCID: PMC10184648
- DOI: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346745
Audio-visual feedback for electromyographic control of vowel synthesis
Abstract
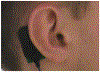
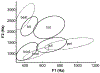
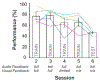
We describe the design and testing of a human machine interface to use surface electromyography (sEMG) collected from a covert location in response audio-visual feedback. Using sEMG collected from the Auricularis Posterior muscle, N=5 healthy participants participated in 6 sessions over multiple days to learn to transition from visual and vowel synthesis feedback to vowel synthesis feedback alone. Results indicate that individuals are able to learn sEMG control of vowel synthesis using auditory feedback alone with an average of 67% accuracy and that this skill can also generalize to new vowel targets. Control of vowel synthesis using covertly-recorded sEMG is a promising step toward more reliable mobile human machine interfaces for communication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of augmentative visual training on audio-motor mapping.Hum Mov Sci. 2014 Jun;35:145-55. doi: 10.1016/j.humov.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Hum Mov Sci. 2014. PMID: 24529925 Free PMC article.
-
Categorical vowel perception enhances the effectiveness and generalization of auditory feedback in human-machine-interfaces.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59860. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059860. Epub 2013 Mar 19. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527278 Free PMC article.
-
The role of augmentative visual training in auditory human-machine-interface performance.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013;2013:2804-7. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2013.6610123. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013. PMID: 24110310
-
[Application progress of surface electromyography and surface electromygraphic biofeedback in low back pain].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Apr 15;31(4):504-507. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201609078. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29798619 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
An intensive neurorehabilitation programme with sEMG biofeedback to improve swallowing in idiopathic Parkinson's disease (IPD): A feasibility study.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 May;58(3):813-825. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12824. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023. PMID: 36478035 Review.
References
-
- Perez-Maldonado C, Wexler AS, and Joshi SS, “Two-dimensional cursor-to-target control from single muscle site sEMG signals,” IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng, vol. 18, pp. 203–9, Apr 2010. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Long J, Yu T, Yu Z, Wang C, Zhang H, and Guan C, “An EEG-based BCI system for 2-D cursor control by combining Mu/Beta rhythm and P300 potential,” IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, vol. 57, pp. 2495–505, Oct 2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
