Flow-dependent vascular heat transfer during microwave thermal ablation
- PMID: 23367194
- PMCID: PMC3563104
- DOI: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6347259
Flow-dependent vascular heat transfer during microwave thermal ablation
Abstract
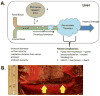
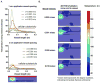
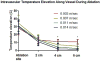
Microwave tumor ablation is an attractive option for thermal ablation because of its inherent benefits over radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in the treatment of solid tumors such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Microwave energy heats tissue to higher temperatures and at a faster rate than RFA, creating larger, more homogenous ablation zones. In this study, we investigate microwave heating near large vasculature using coupled fluid-flow and thermal analysis. Low-flow conditions are predicted to be more likely to cause cytotoxic heating and, therefore, vessel thrombosis and endothelial damage of downstream tissues. Such conditions may be more prevalent in patient with severe cirrhosis or compromised blood flow. High-flow conditions create the more familiar heat-sink effect that can protect perivascular tissues from the intended thermal damage. These results may help guide placement and use of microwave ablation technologies in future studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heat sink effect on tumor ablation characteristics as observed in monopolar radiofrequency, bipolar radiofrequency, and microwave, using ex vivo calf liver model.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Mar;94(9):e580. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000580. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 25738477 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Microwave Ablation (MWA) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) in Difficult Anatomical Sites in Egyptian Patients with Liver Cirrhosis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019 Jan 25;20(1):295-301. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.1.295. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019. PMID: 30678453 Free PMC article.
-
Small single perivascular hepatocellular carcinoma: comparisons of radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation by using propensity score analysis.Eur Radiol. 2021 Jul;31(7):4764-4773. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07571-5. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33399908 Free PMC article.
-
Radiofrequency Ablation and Microwave Ablation in Liver Tumors: An Update.Oncologist. 2019 Oct;24(10):e990-e1005. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0337. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 31217342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Percutaneous ablation for perivascular hepatocellular carcinoma: Refining the current status based on emerging evidence and future perspectives.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Dec 21;24(47):5331-5337. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i47.5331. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30598578 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dielectric Properties of Ovine Heart at Microwave Frequencies.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Mar 16;11(3):531. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11030531. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809672 Free PMC article.
-
Current perspectives on microwave ablation of liver lesions in difficult locations.J Clin Imaging Sci. 2022 Dec 1;12:61. doi: 10.25259/JCIS_126_2022. eCollection 2022. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2022. PMID: 36601606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can we ablate liver lesions close to large portal and hepatic veins with MR-guided HIFU? An experimental study in a porcine model.Eur Radiol. 2019 Sep;29(9):5013-5021. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5996-8. Epub 2019 Feb 8. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30737565
-
Potential Mechanisms of Vascular Thrombosis after Microwave Ablation in an in Vivo Liver.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017 Jul;28(7):1053-1058. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2017.03.034. Epub 2017 Apr 26. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28456355 Free PMC article.
-
Computational modelling of microwave tumour ablations.Int J Hyperthermia. 2013 Jun;29(4):308-17. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2013.799295. Int J Hyperthermia. 2013. PMID: 23738698 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pisa S, Cavagnaro M, Bernardi P, Lin JC. A 915-MHz antenna for microwave thermal ablation treatment: physical design, computer modeling and experimental measurement. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2001 May;48(no. 5):599–601. - PubMed
-
- Brace CL, Laeseke PF, Sampson LA, Frey TM, van der Weide DW, Lee FT. Microwave Ablation with Multiple Simultaneously Powered Small-gauge Triaxial Antennas: Results from an in Vivo Swine Liver Model1. Radiology. 2007 Jul;244(no. 1):151–156. - PubMed
-
- Lu DSK, Raman SS, Vodopich DJ, Wang M, Sayre J, Lassman C. Effect of vessel size on creation of hepatic radiofrequency lesions in pigs: assessment of the ‘heat sink’ effect. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002 Jan;178(no. 1):47–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
