Leflunomide inhibits the apoptosis of human embryonic lung fibroblasts infected by human cytomegalovirus
- PMID: 23369524
- PMCID: PMC3598351
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783X-18-3
Leflunomide inhibits the apoptosis of human embryonic lung fibroblasts infected by human cytomegalovirus
Abstract
Background: The immunomodulatory drug leflunomide (LEF) is frequently used for treating human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), but its antiviral mechanism is still unclear. In this study,we therefore investigated the effects of the active LEF metabolite A771726 on the HCMV lifecycle in human embryonic lung fibroblasts. We clarified the mechanism of LEF antiviral infection, and provide a new way to treat immune dysfunction patients with HCMV infection.
Methods: The experiment was divided into four groups: the control group, the HCMV group, the ganciclovir+HCMV group as well as the LEF+HCMV group. MTT was used for assessment of the cell inhibitory rate. Apoptosis was measured by staining with fluorescein isothiocyanate Annexin V and propidium iodide. Statistical significance was determined by paired t-test using SPSS software.
Results: The results of the study showed that cell proliferation was significantly inhibited by HCMV at 24 hours and 48 hours. With increasing HCMV concentration, the value-added inhibition of the cells was significantly decreased compared with the control group, and was statistically significant (P<0.01). Ganciclovir can increase proliferation of cells infected with HCMV; compared with the control group it was statistically significant (P<0.05). Meanwhile, with LEF treatment cell proliferation was significantly improved at 24 hours and 48 hours, with statistical significance (P<0.05). The apoptosis rate of human embryonic lung fibroblasts infected with HCMV increased significantly at 24 hours, 48 hours and 72 hours, and as time goes on the apoptosis rate increases statistically significantly (P<0.01) compared with the control group The apoptosis rate of the HCMV infection group decreased by adding LEF,and was statistically significant (P<0.05).
Conclusions: In this study we show that LEF is an exciting new drug for cytomegalovirus infection. LEF significantly inhibited HCMV infection-induced apoptosis and proliferation, playing an important role in the treatment of patients infected by HCMV. In this study we explored the potential usefulness of LEF for cytomegalovirus infection and found it to be a cost-effective new treatment for cytomegalovirus infection that deserves further study.
Figures
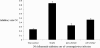


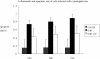
Similar articles
-
Apoptosis Disorder, a Key Pathogenesis of HCMV-Related Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 15;22(8):4106. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084106. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of human cytomegalovirus infection on apoptosis and expression of apoptosis-regulating factors.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2005;25(5):480-3. doi: 10.1007/BF02895993. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2005. PMID: 16463650
-
Apoptosis induced by human cytomegalovirus infection can be enhanced by cytokines to limit the spread of virus.Exp Hematol. 1999 Jul;27(7):1194-203. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(99)00044-2. Exp Hematol. 1999. PMID: 10390195
-
Inhibition of Cytomegalovirus Replication with Extended-Half-Life Synthetic Ozonides.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Dec 21;63(1):e01735-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01735-18. Print 2019 Jan. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30373792 Free PMC article.
-
[Interrelationship between human cytomegalovirus infection and chemokine].Nihon Rinsho. 1998 Jan;56(1):69-74. Nihon Rinsho. 1998. PMID: 9465667 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Current and potential treatments for ubiquitous but neglected herpesvirus infections.Chem Rev. 2014 Nov 26;114(22):11382-412. doi: 10.1021/cr500255e. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Chem Rev. 2014. PMID: 25275644 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Apoptosis Disorder, a Key Pathogenesis of HCMV-Related Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 15;22(8):4106. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084106. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-senescence effect and molecular mechanism of the major royal jelly proteins on human embryonic lung fibroblast (HFL-I) cell line.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2018 Dec.;19(12):960-972. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1800257. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2018. PMID: 30507079 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-viral facet of anti-rheumatic drugs: Lessons from COVID-19.J Autoimmun. 2020 Jul;111:102468. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102468. Epub 2020 Apr 17. J Autoimmun. 2020. PMID: 32317220 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

